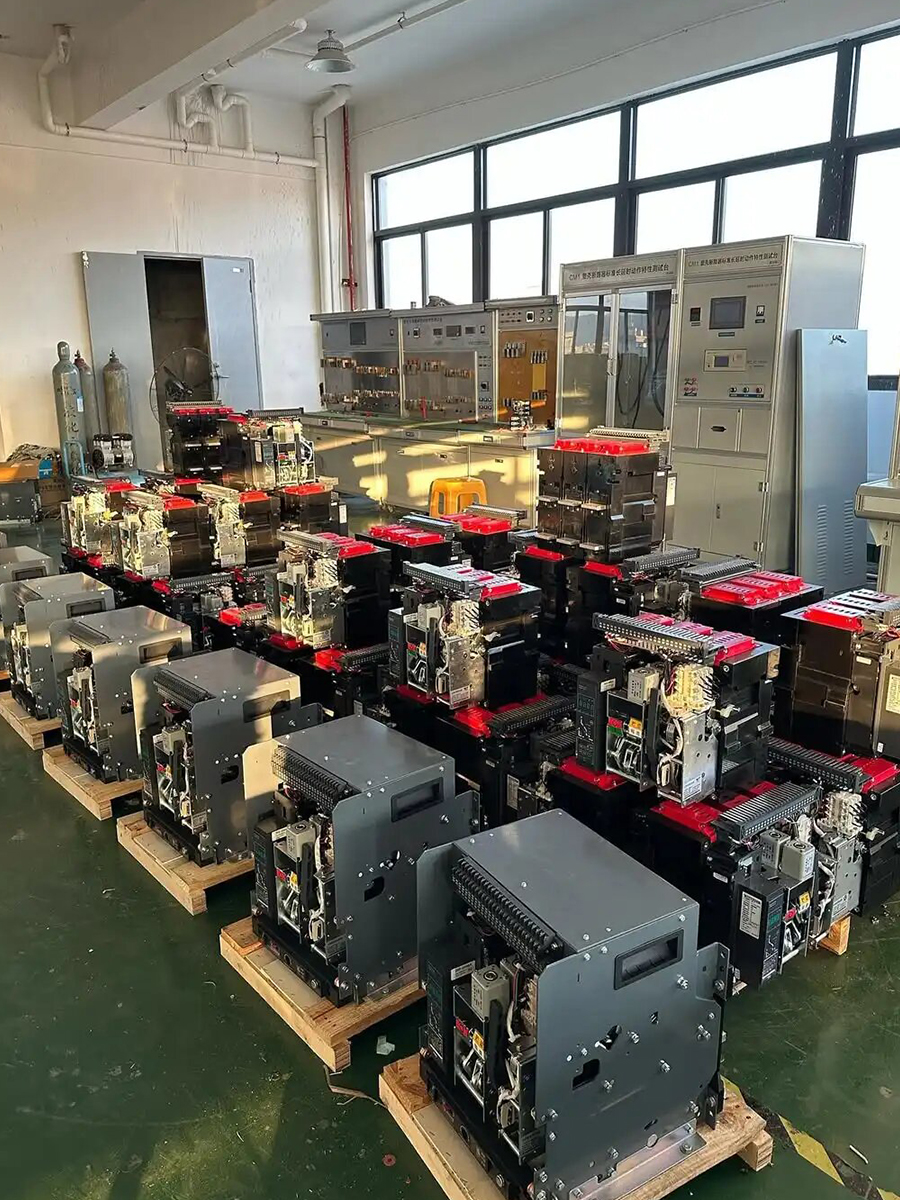
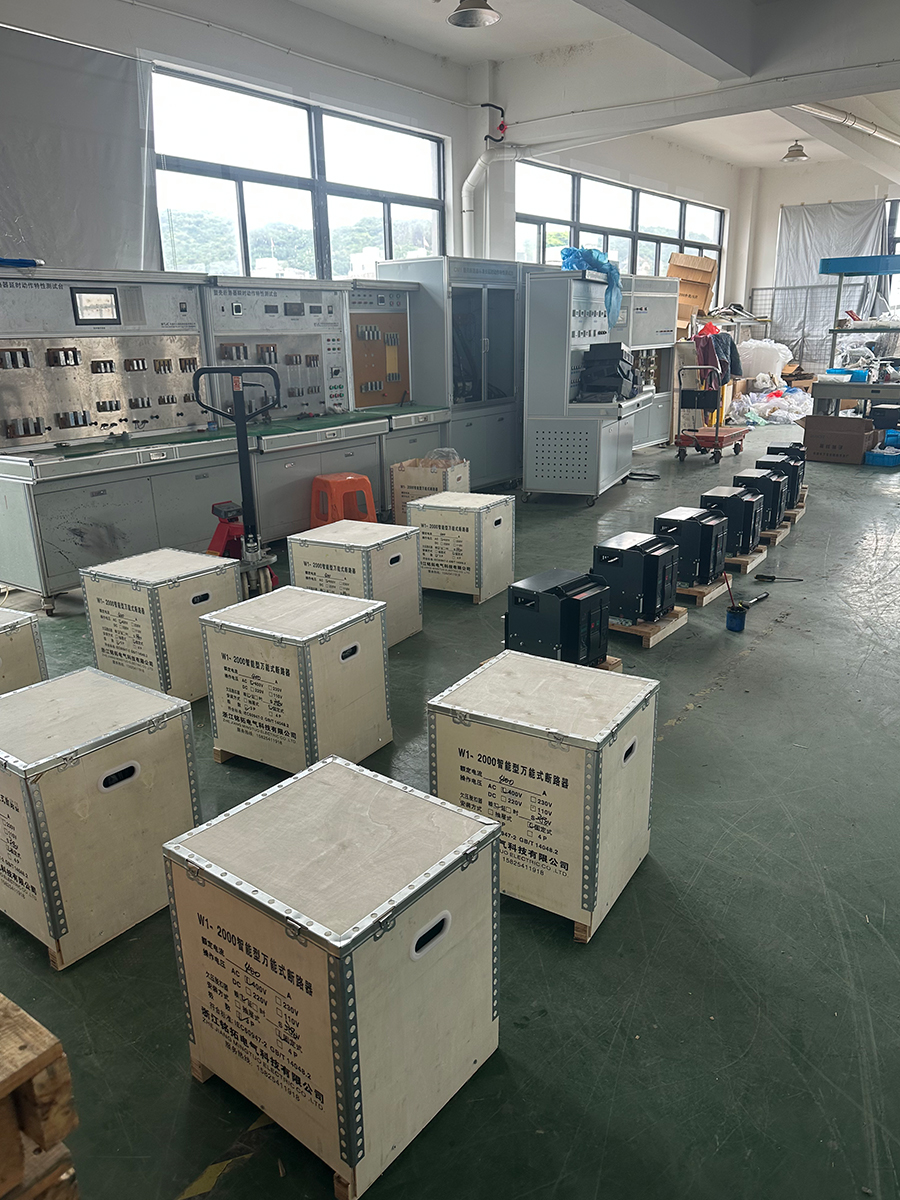
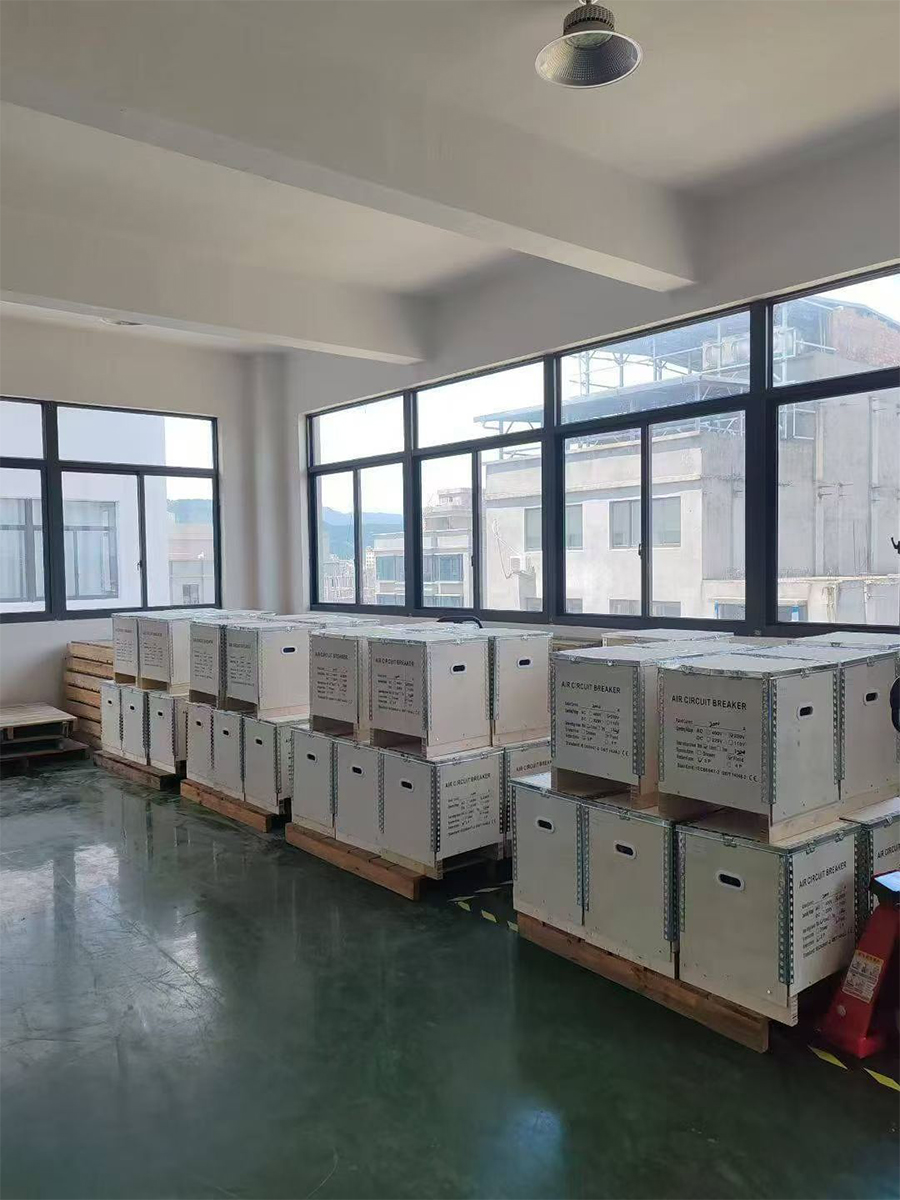
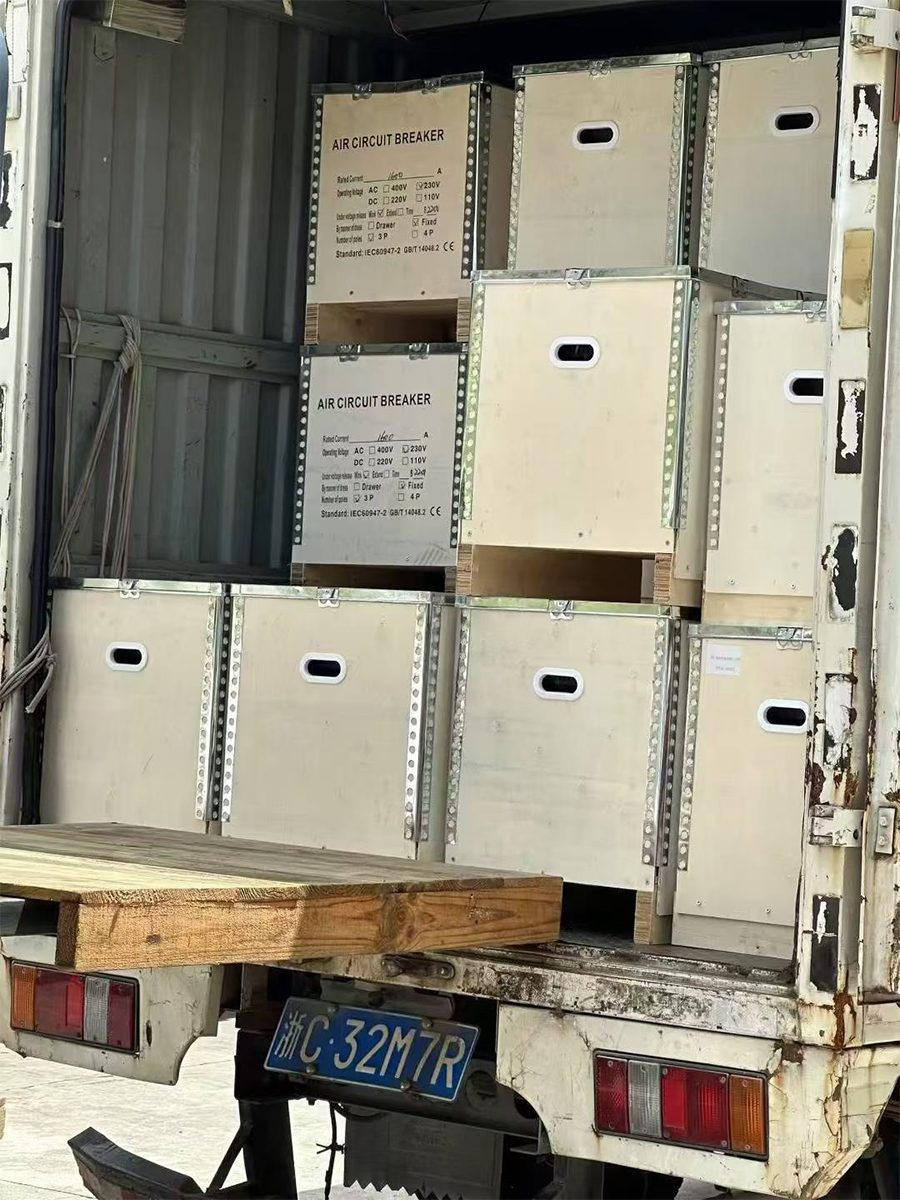
- ACB installation And Test
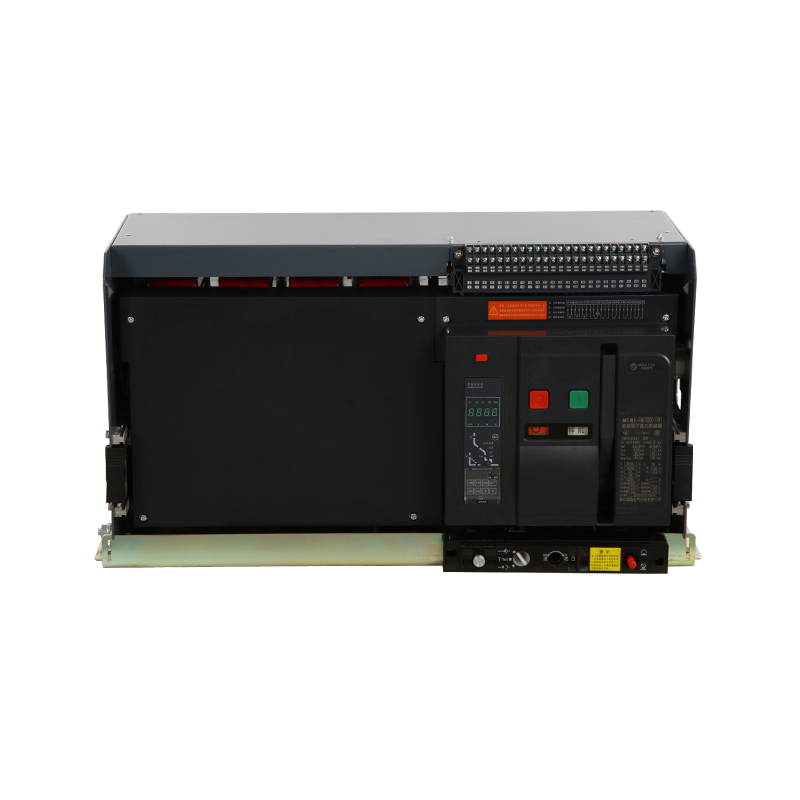
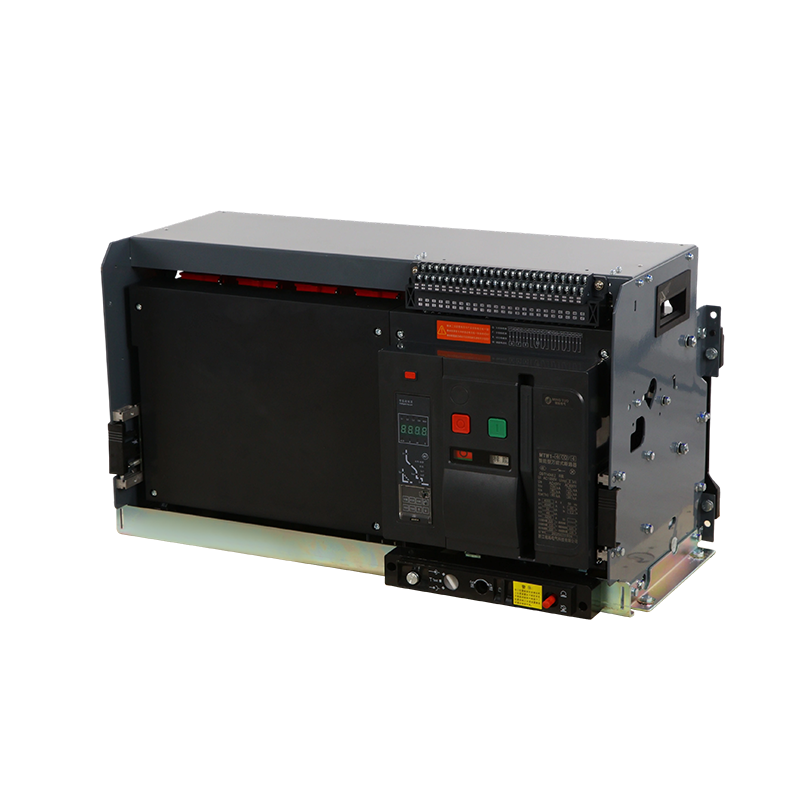
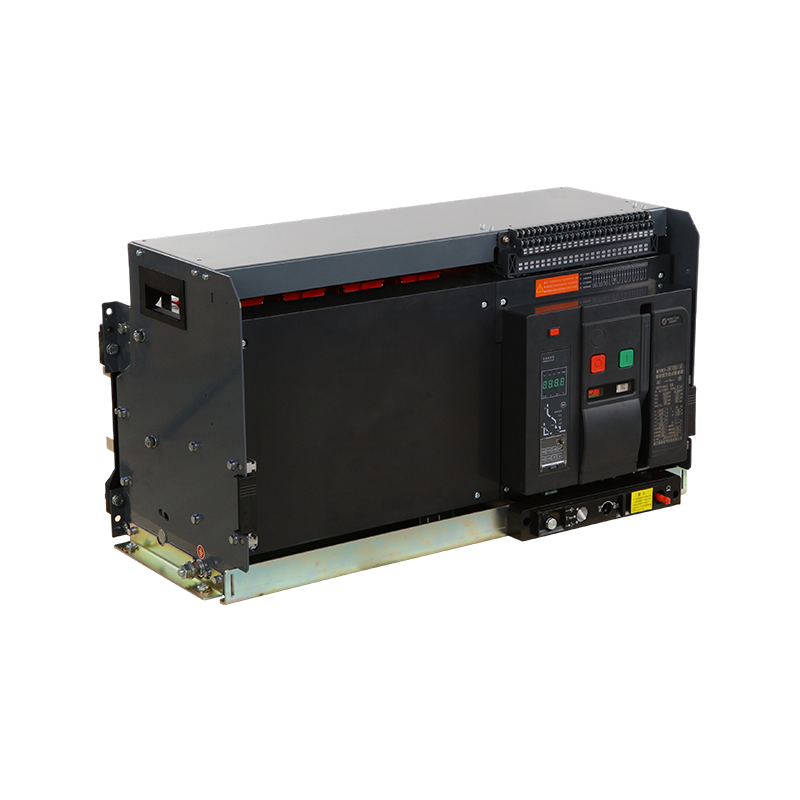
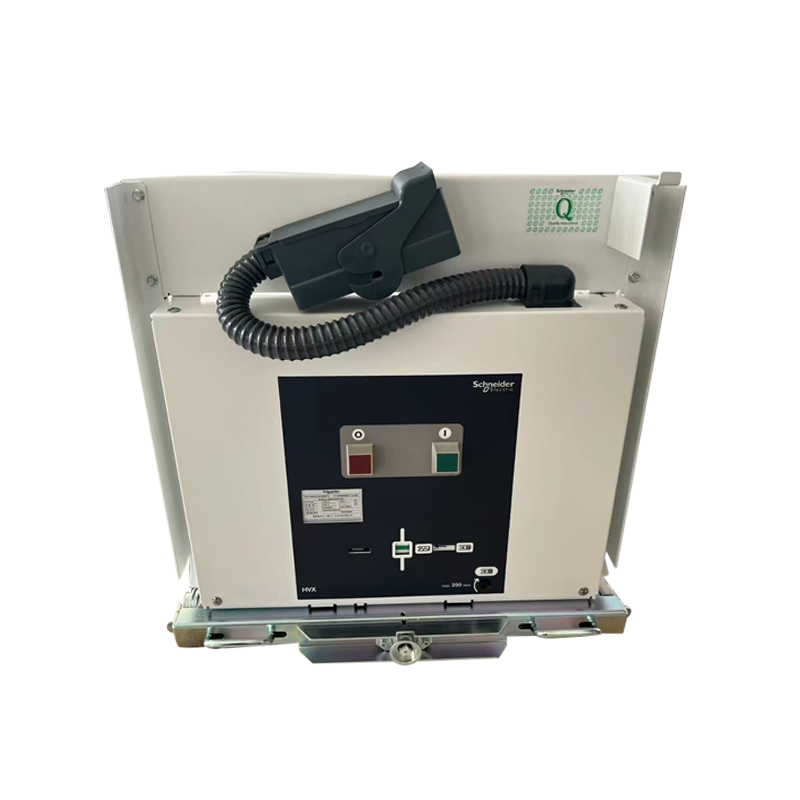
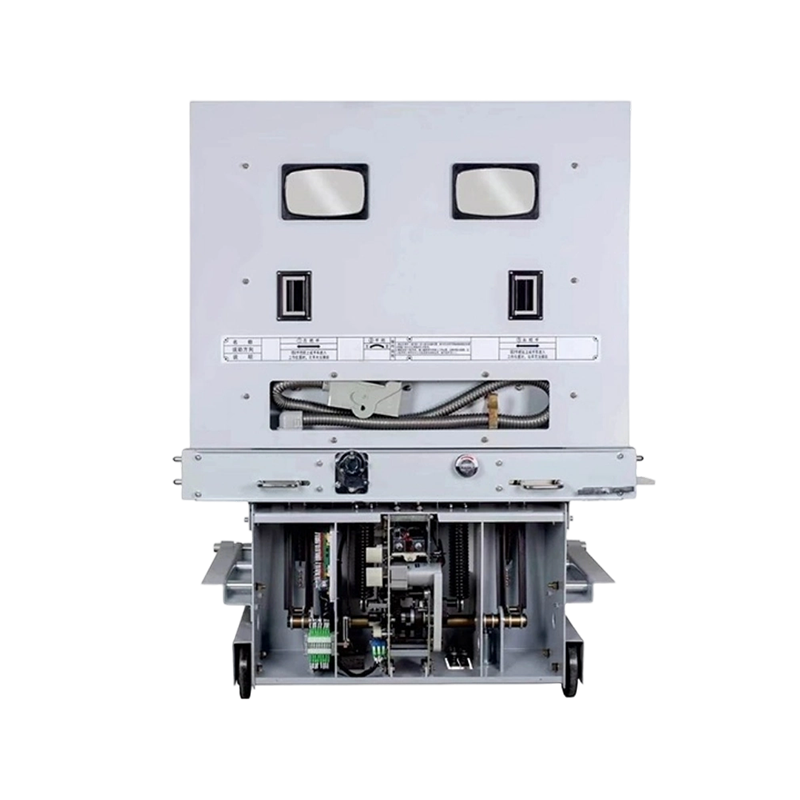
- ACB Installation
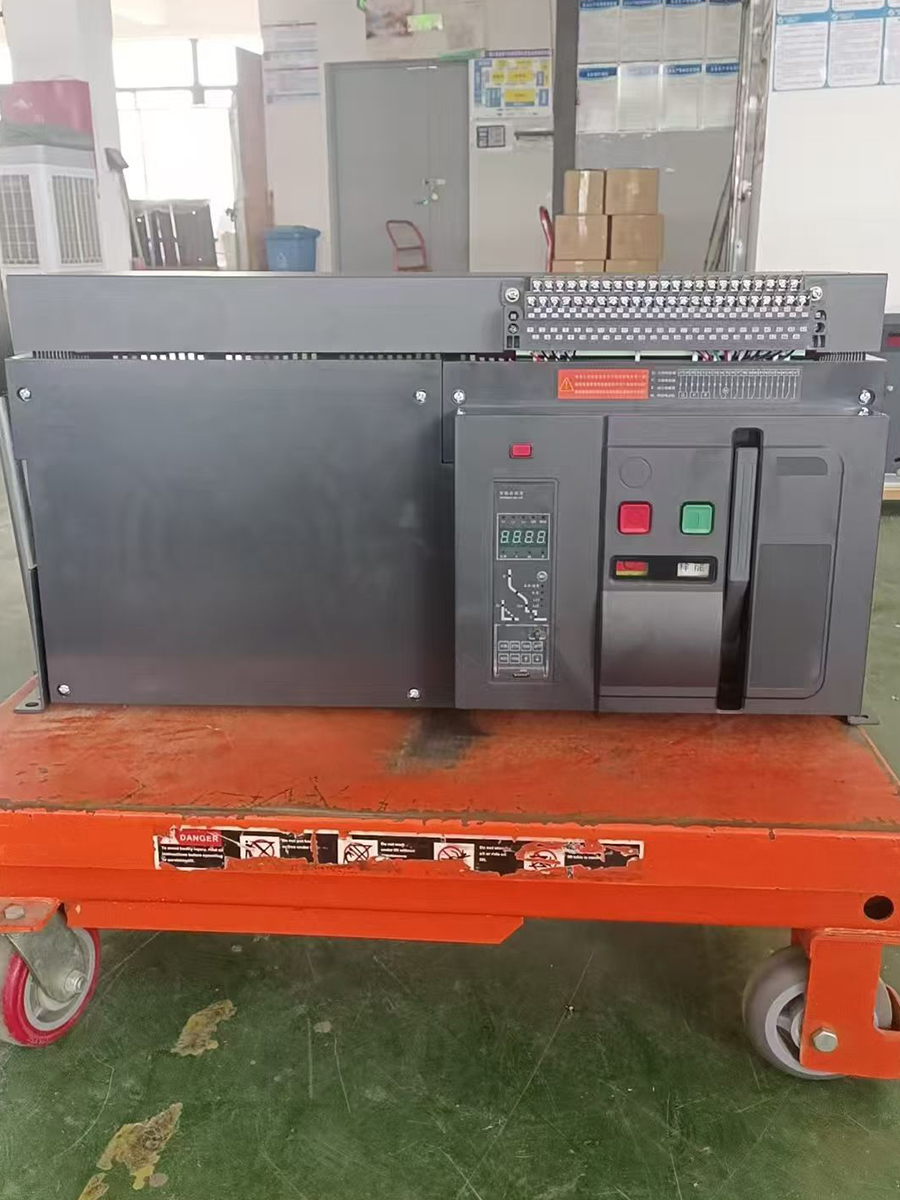
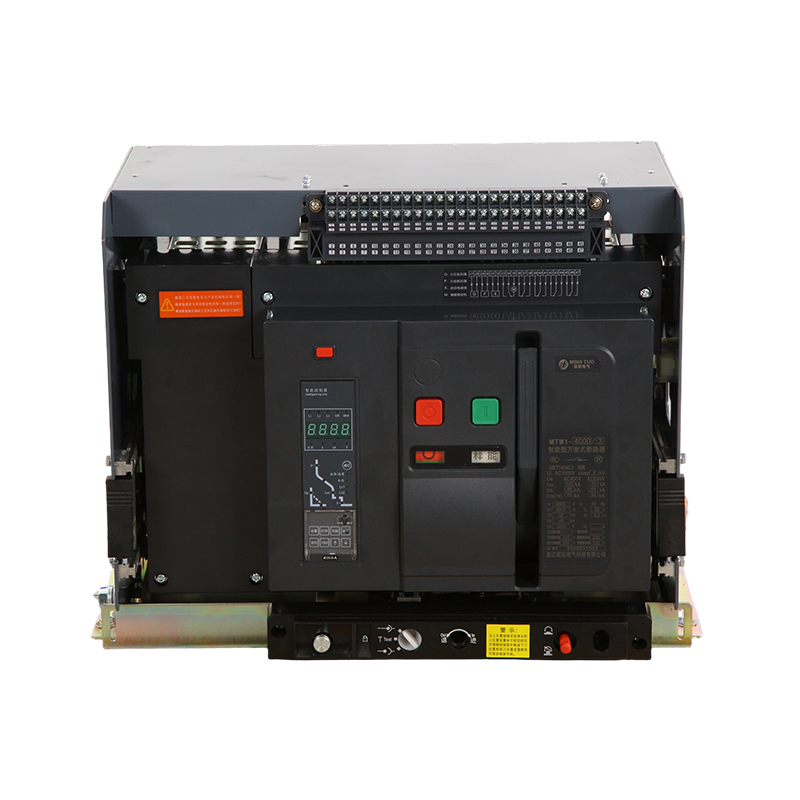
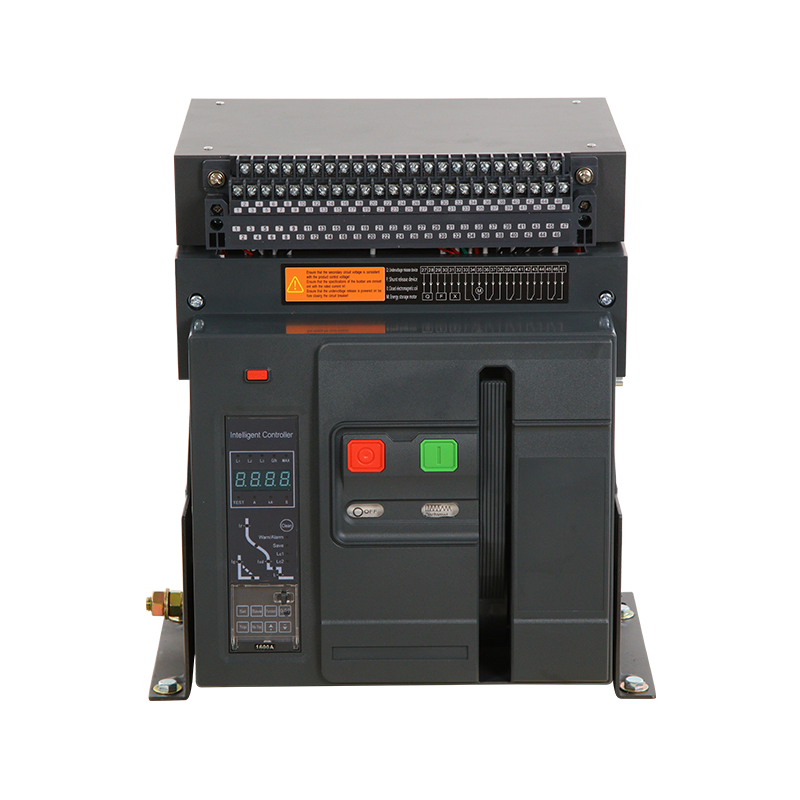
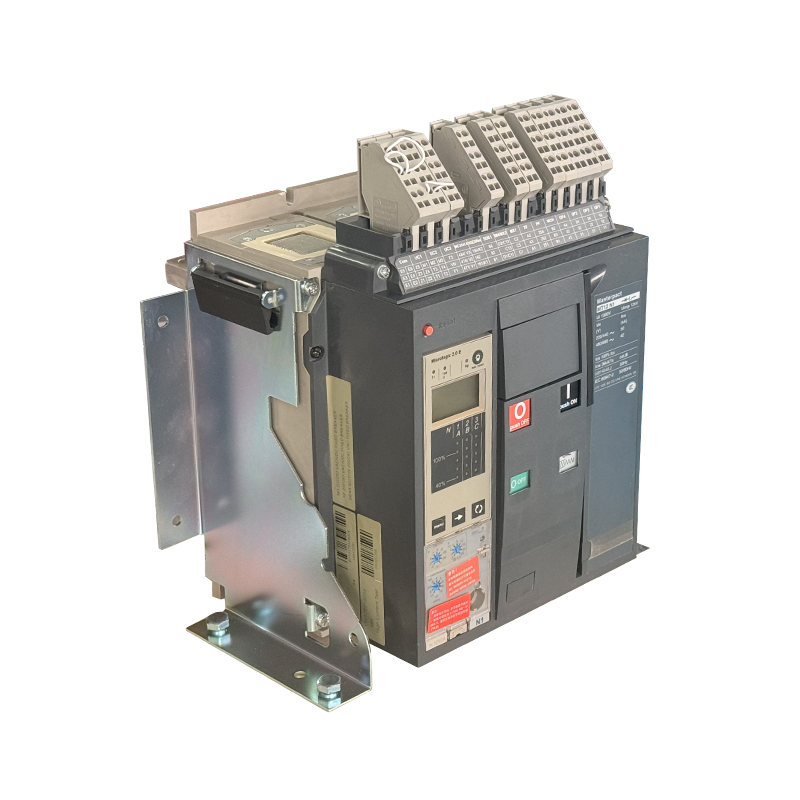
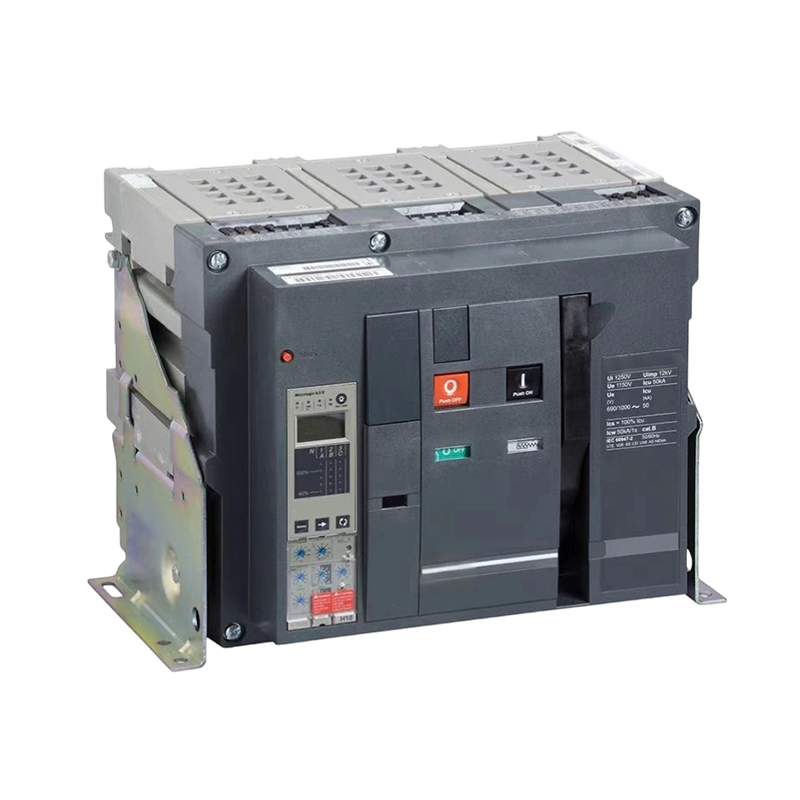
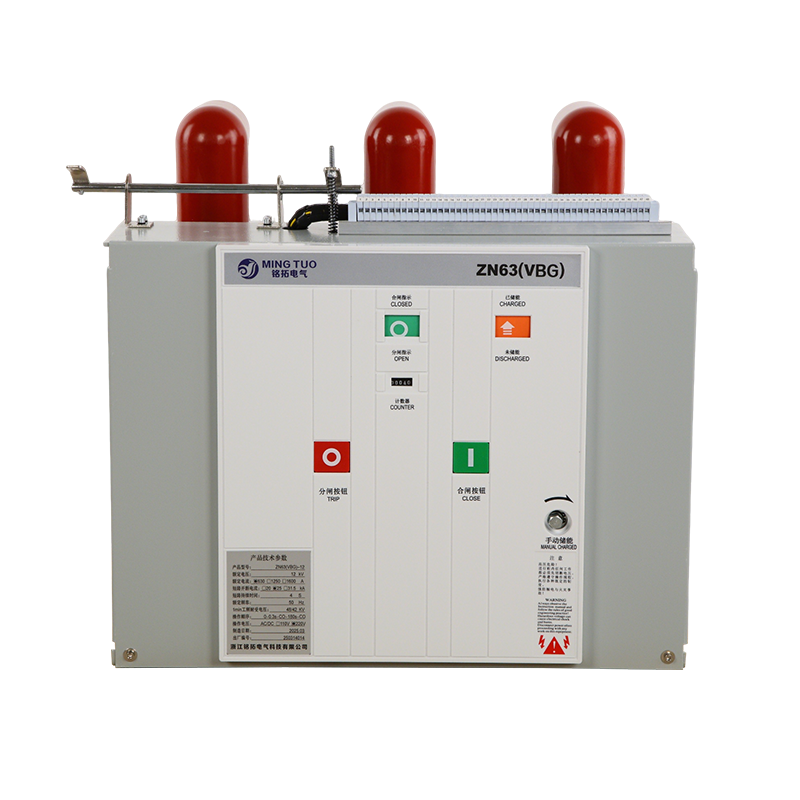
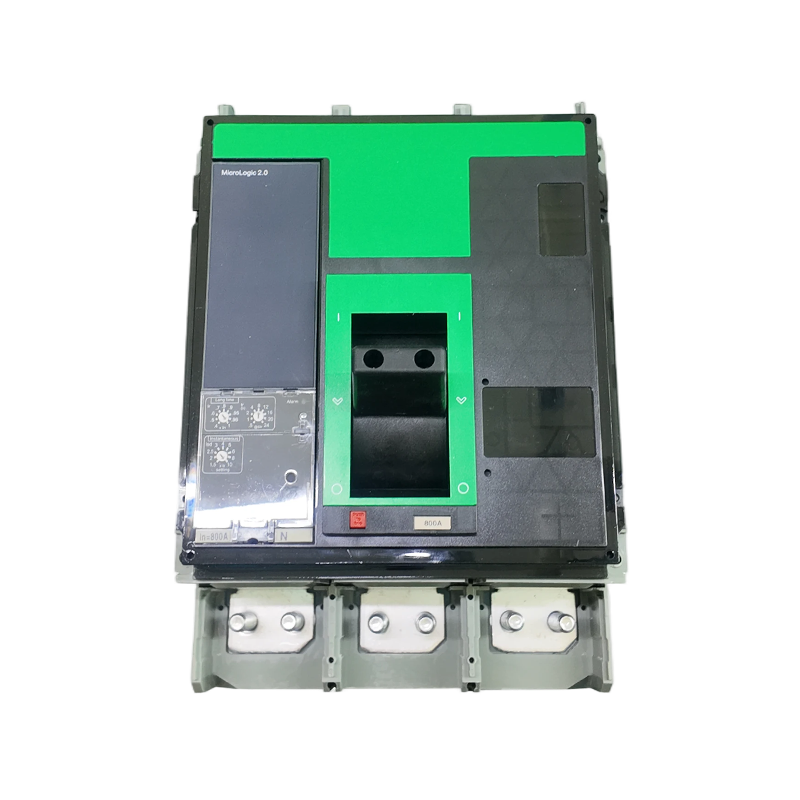
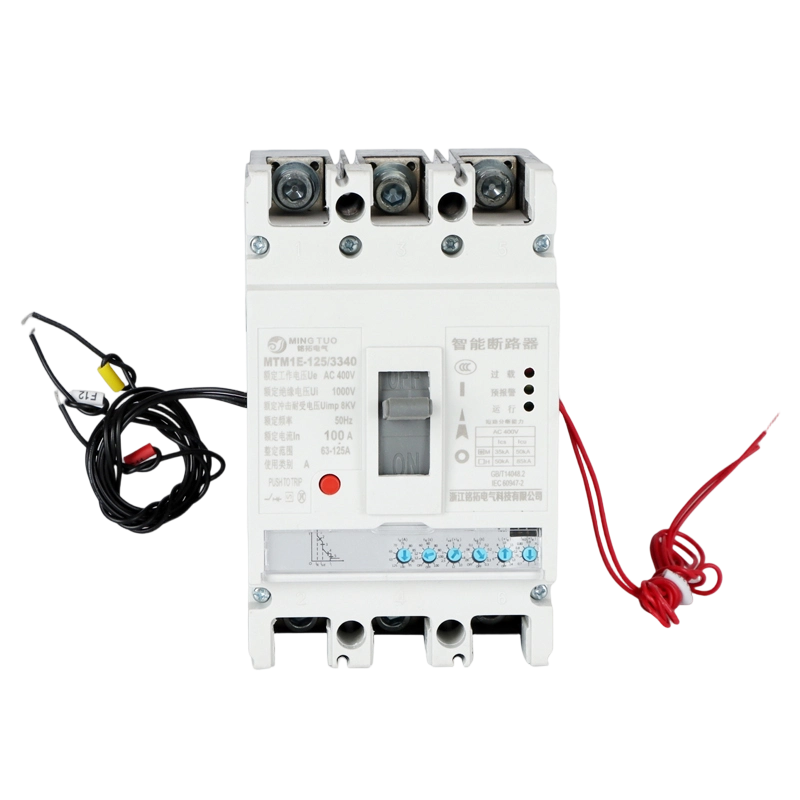
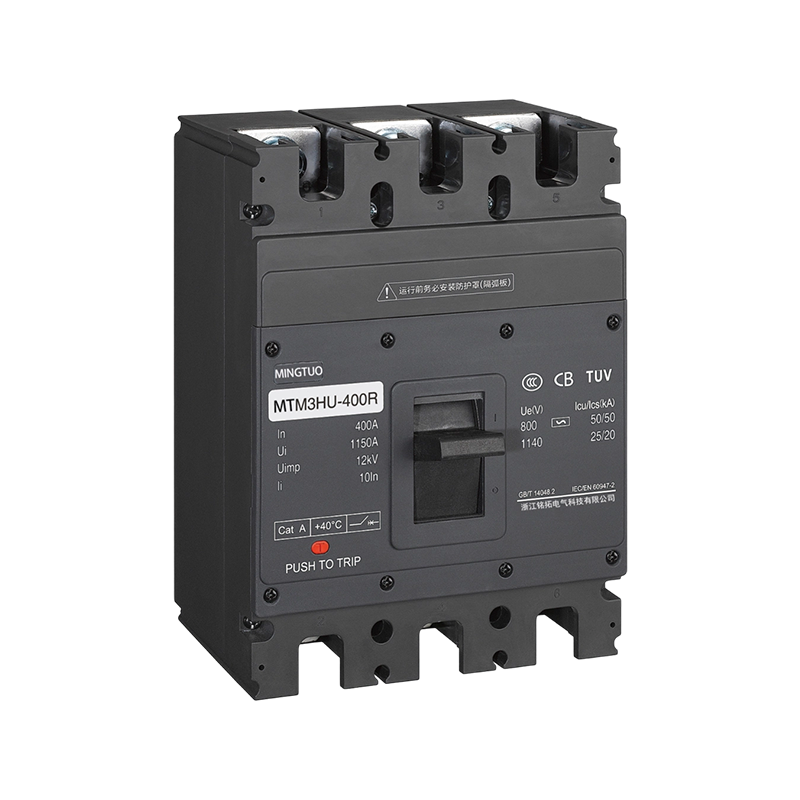
- ACB
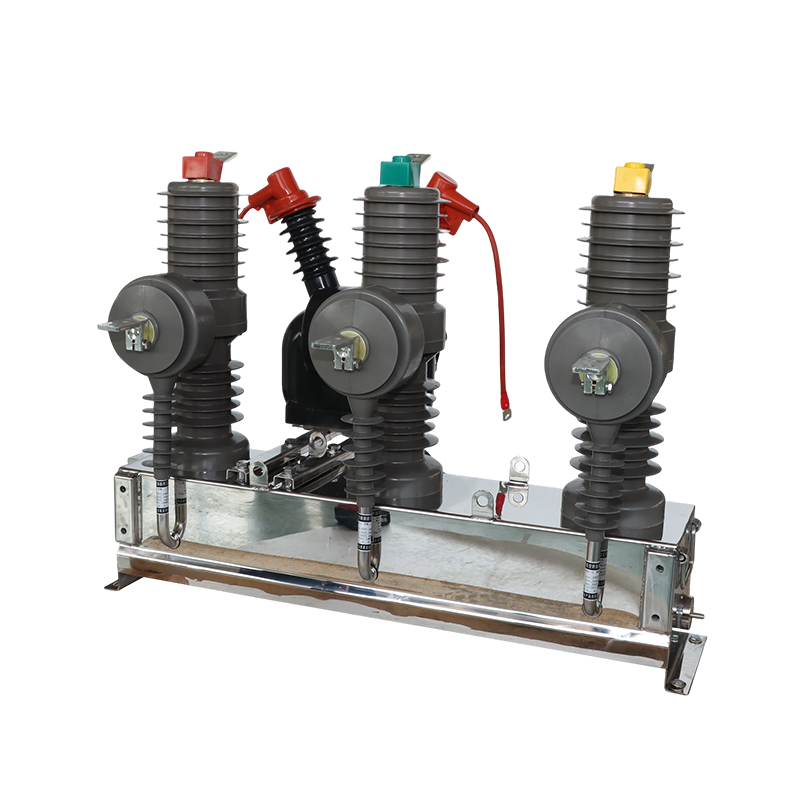
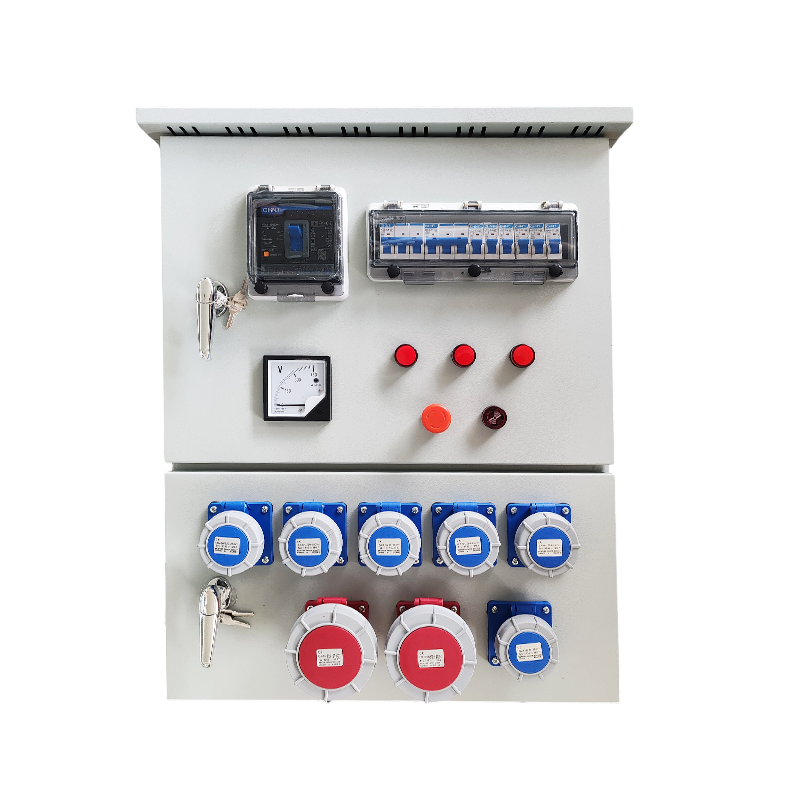
- Double Circuit Breakerswitching Cabinet
- Working Principle
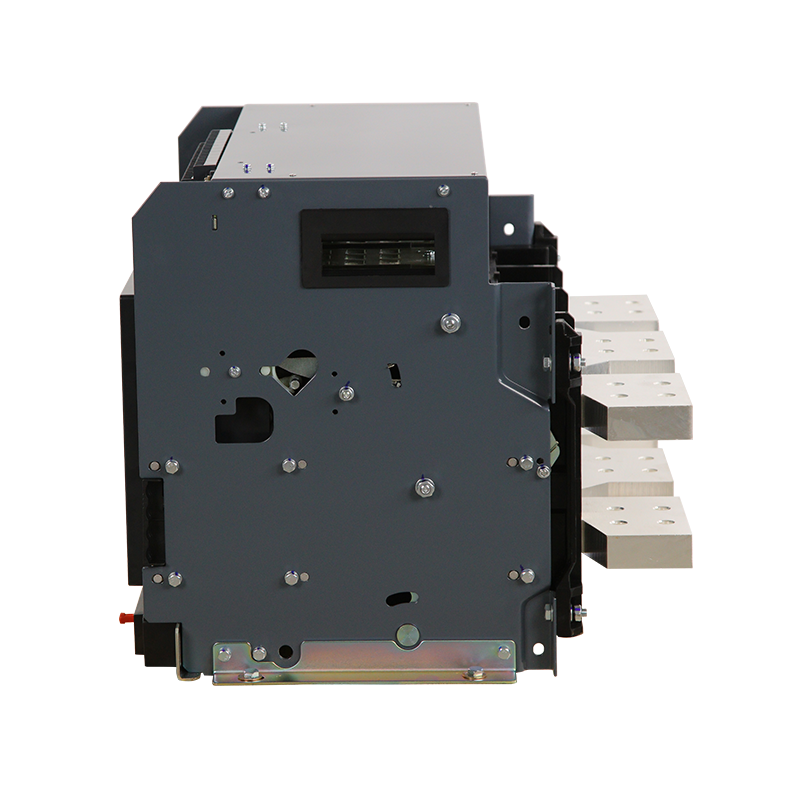
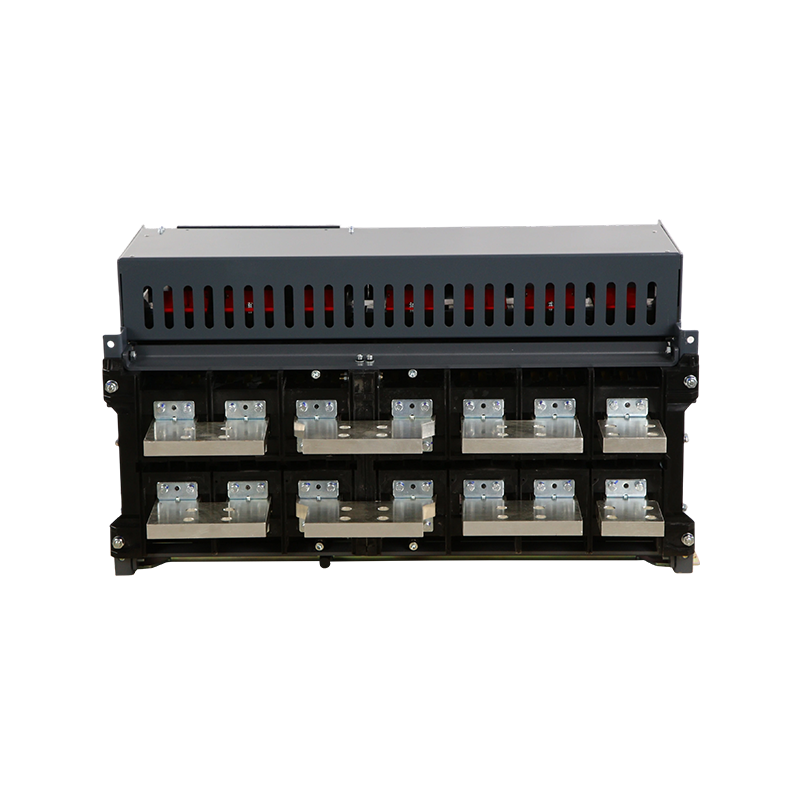
- Moving And Static Contact
- ACB Machanism
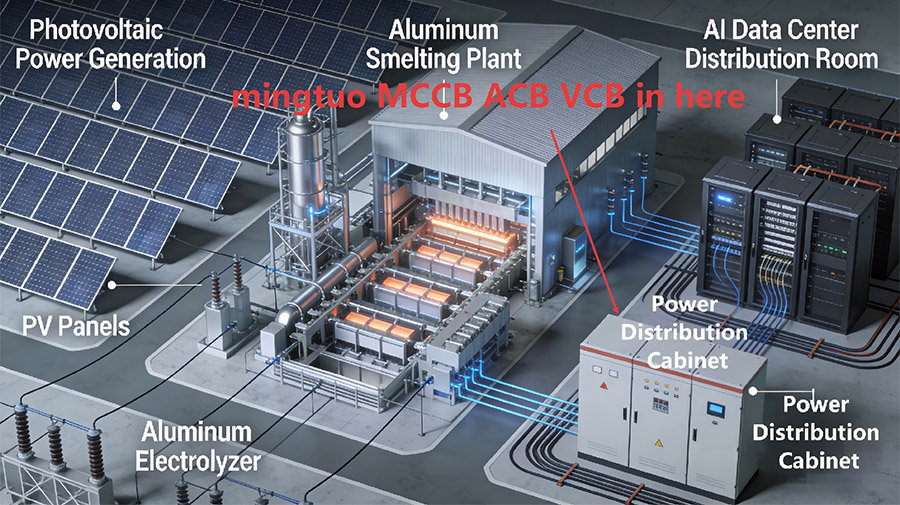
When the product is in the closed and powered on state, if there is overload or short circuit, undervoltage or phase loss in the circuit, the current transformer in the ACB will detect the current signal, which will be transmitted to the controller. The controller will then send a command to the mechanism to trip, causing the dynamic and static contacts to separate and disconnect, and the product will open, achieving the function of protecting the backend load.
Dual power supply realizes mechanical and electrical interlocking, switching between two power supply lines. When the mains power is available, the circuit breaker of the mains power is closed, but the power generation cannot be closed. When the mains power is cut off, the generator generates power, and the circuit breaker of the power generation line is closed, but the mains power cannot be closed. Only one of the two power sources can be closed.
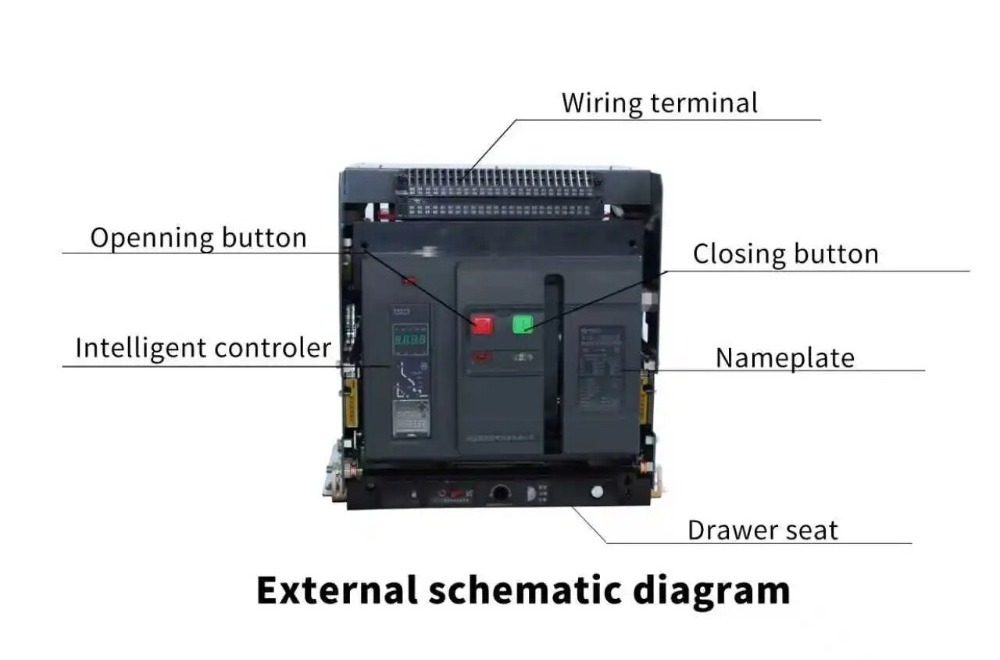 |
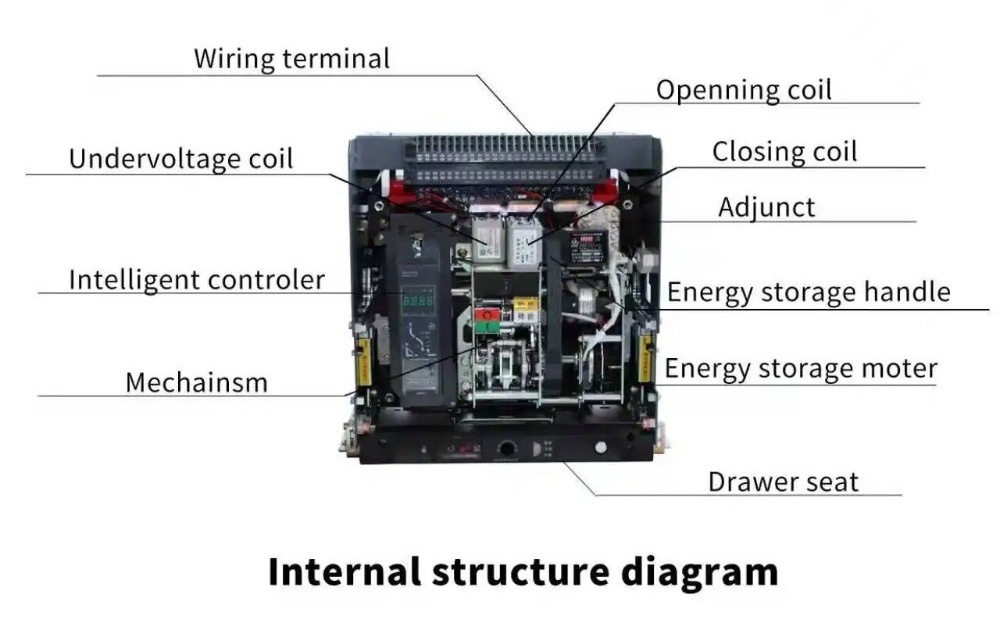 |



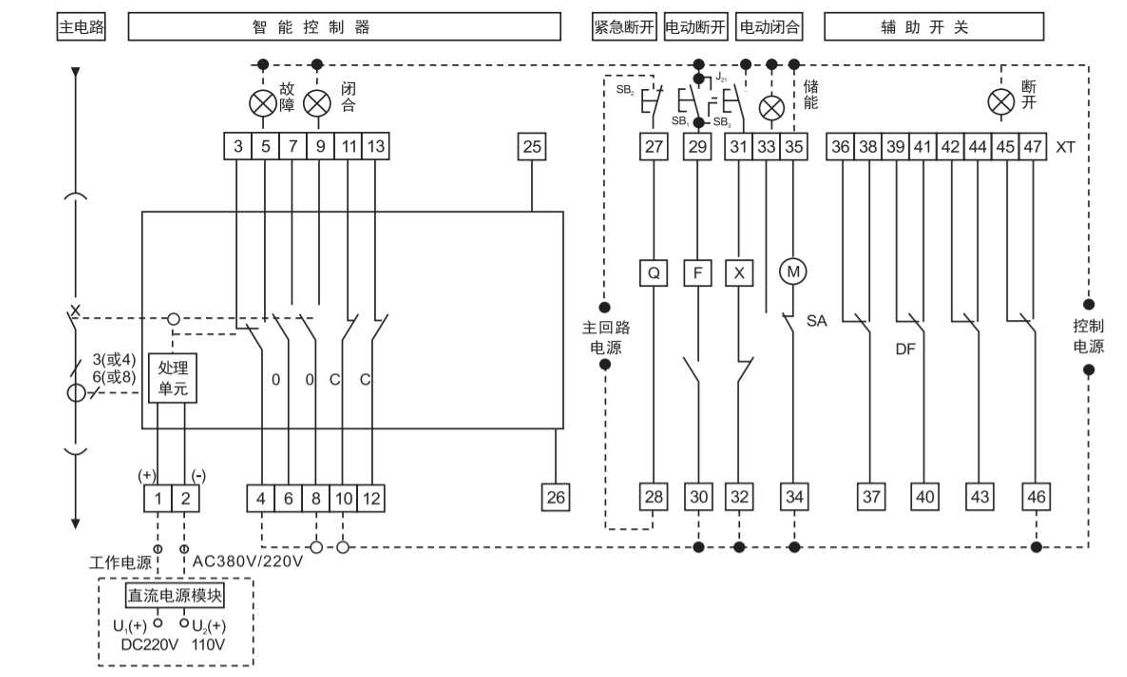
-
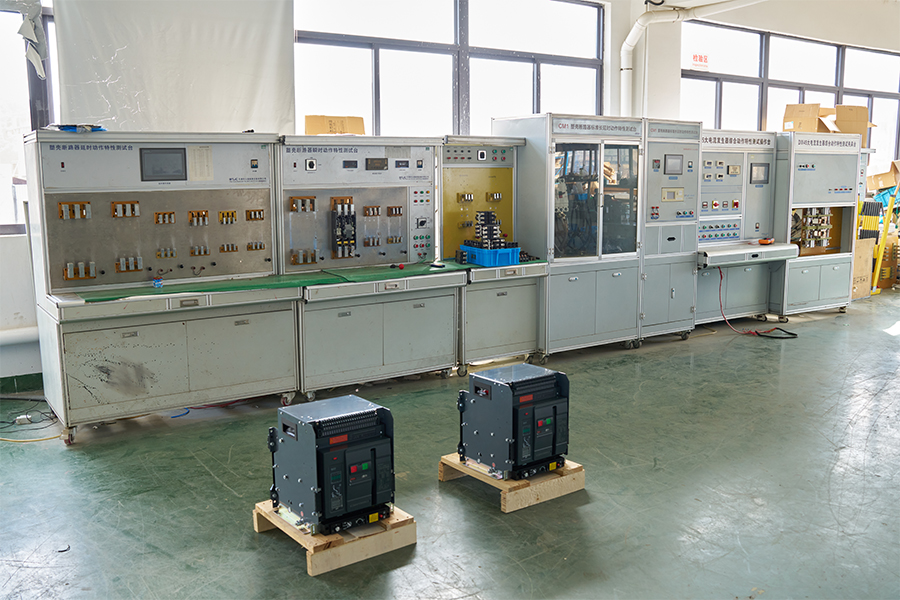 ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
-
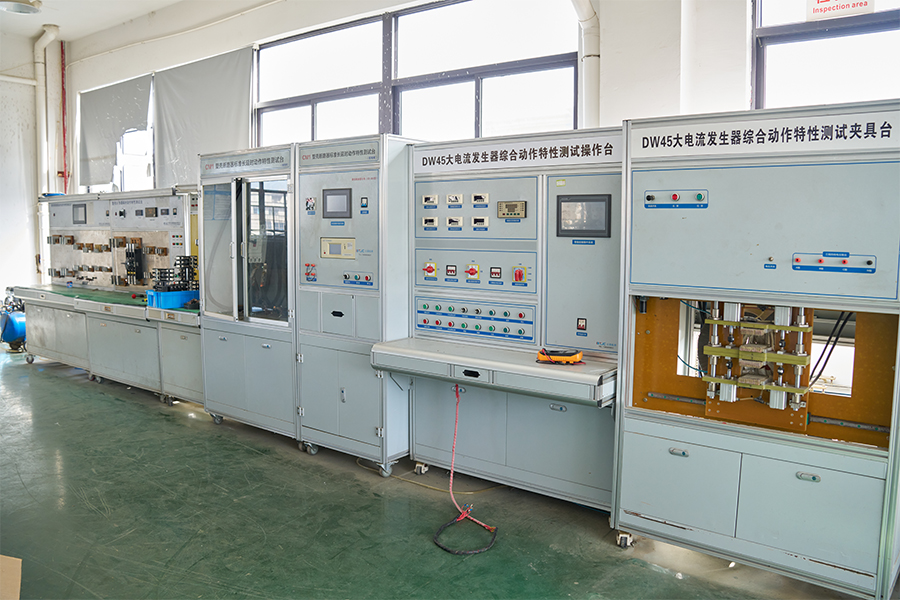 ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
-
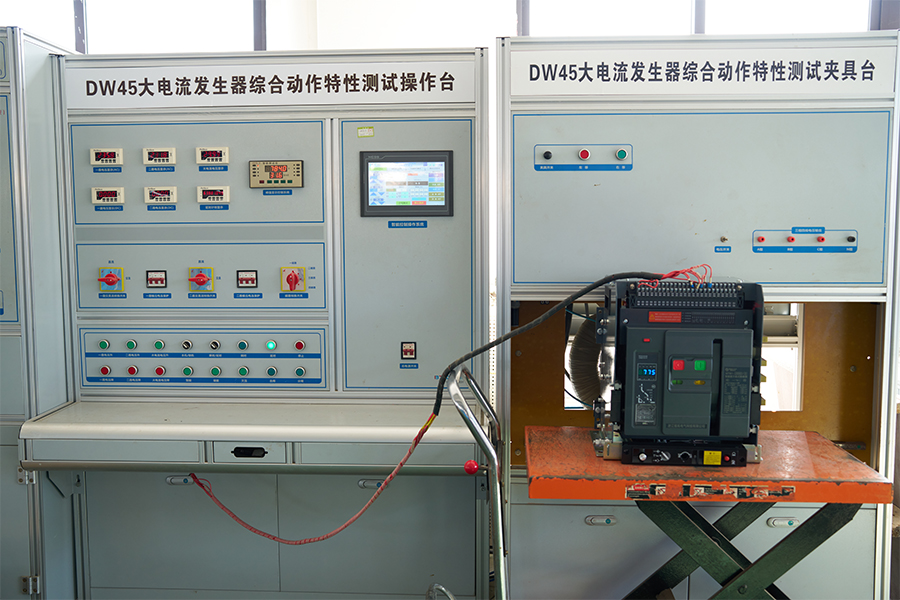 ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
-
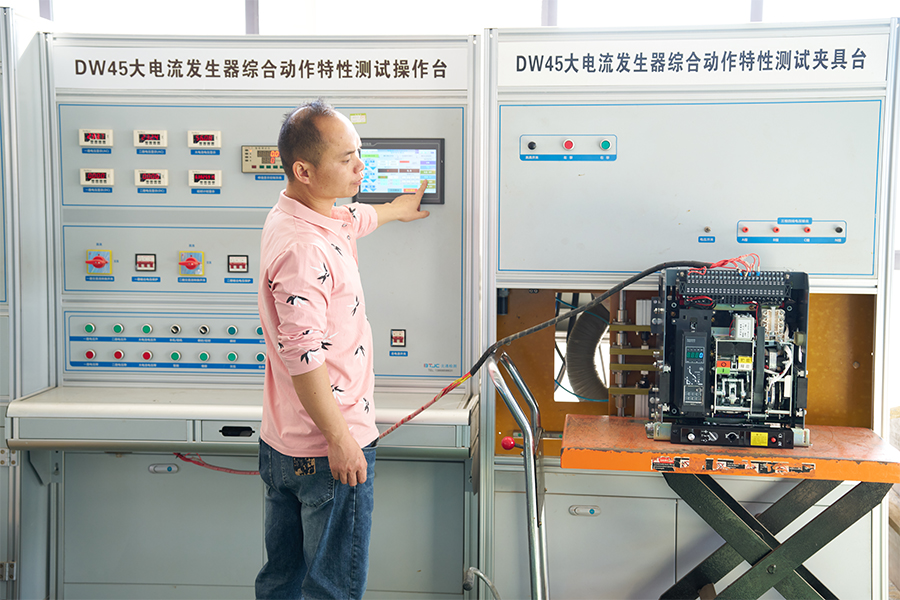 ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
-
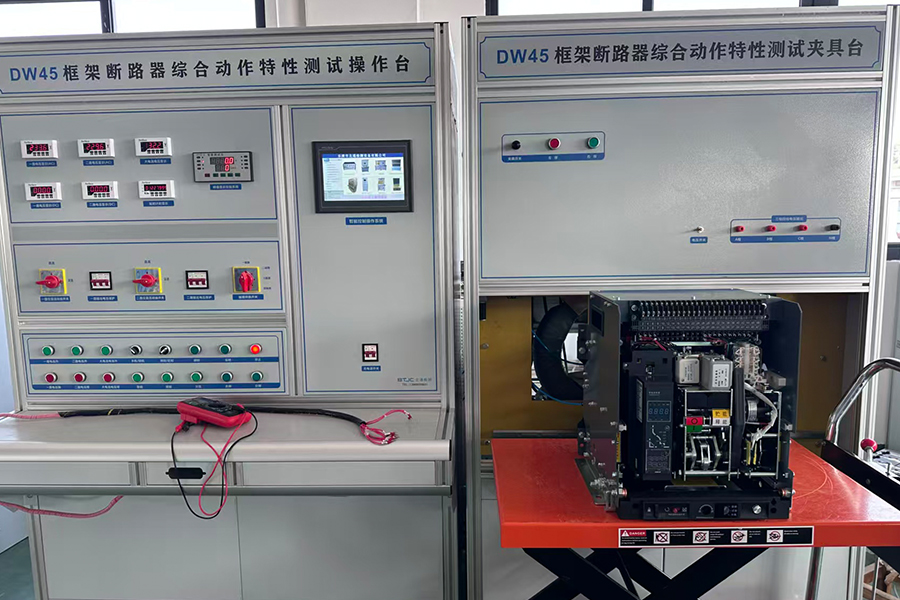 ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
ACB Closing/Opening - Energy Storage - Overload - Short Circuit - Undervoltage Testing
To ensure transportation safety, our electrical products are exported in reinforced wooden crates. The crates undergo heat treatment and bear the ISPM-15 mark, enabling swift customs clearance. The raised base design facilitates forklift operation, while internal shock-absorbing fastening ensures the products arrive intact. All exterior crates are clearly labeled and comply with international logistics standards.
-
 Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Cabinet Utilising ACB and MCCB
Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Cabinet Utilising ACB and MCCB
-
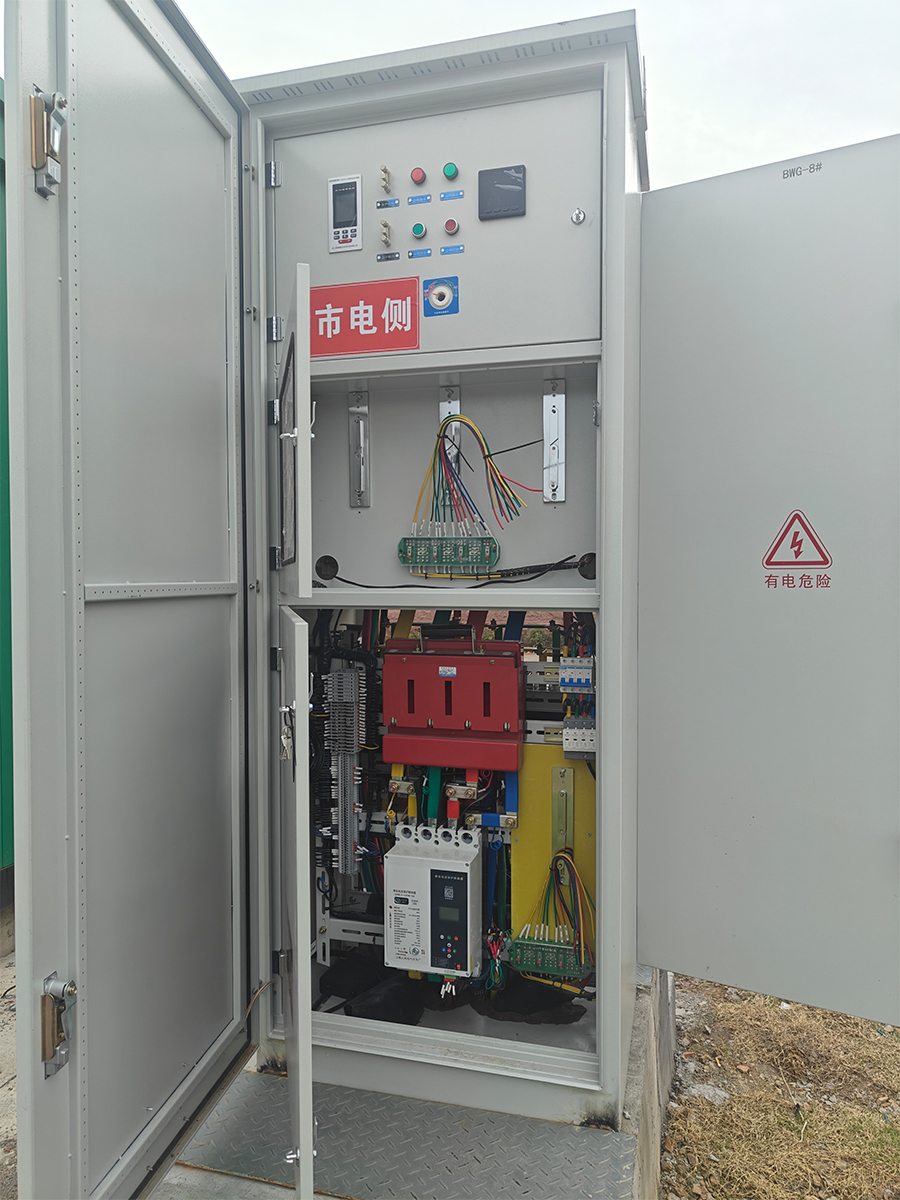 Power transmission successful
Power transmission successful
-
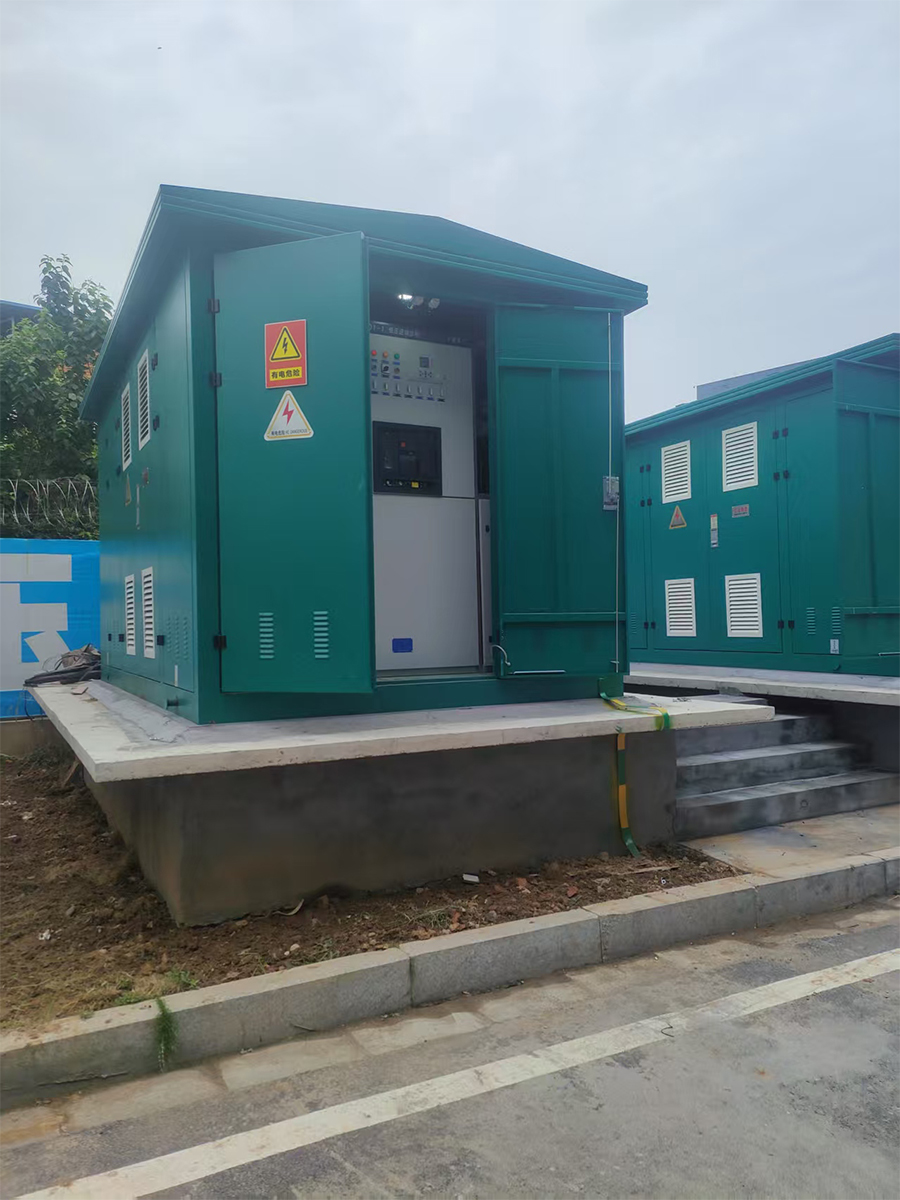 Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
-
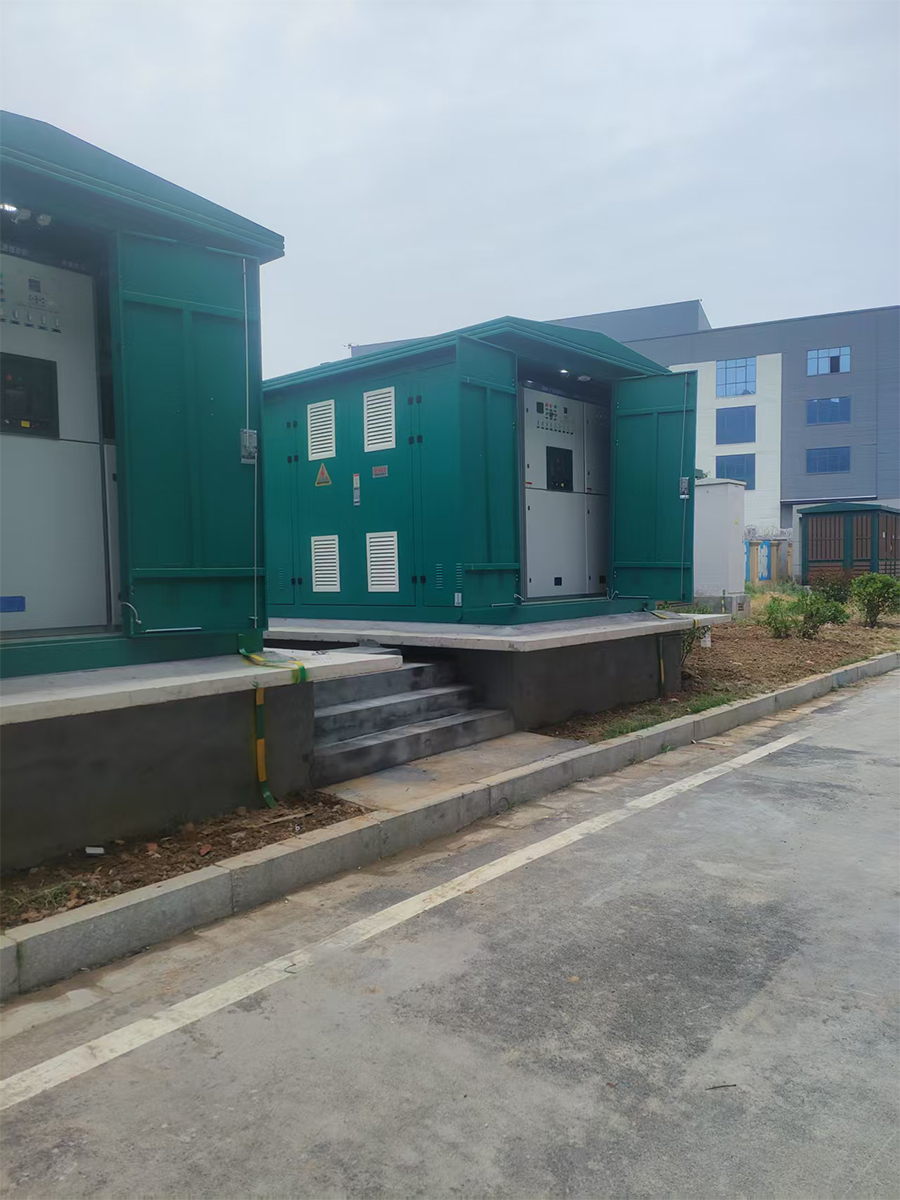 Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
-
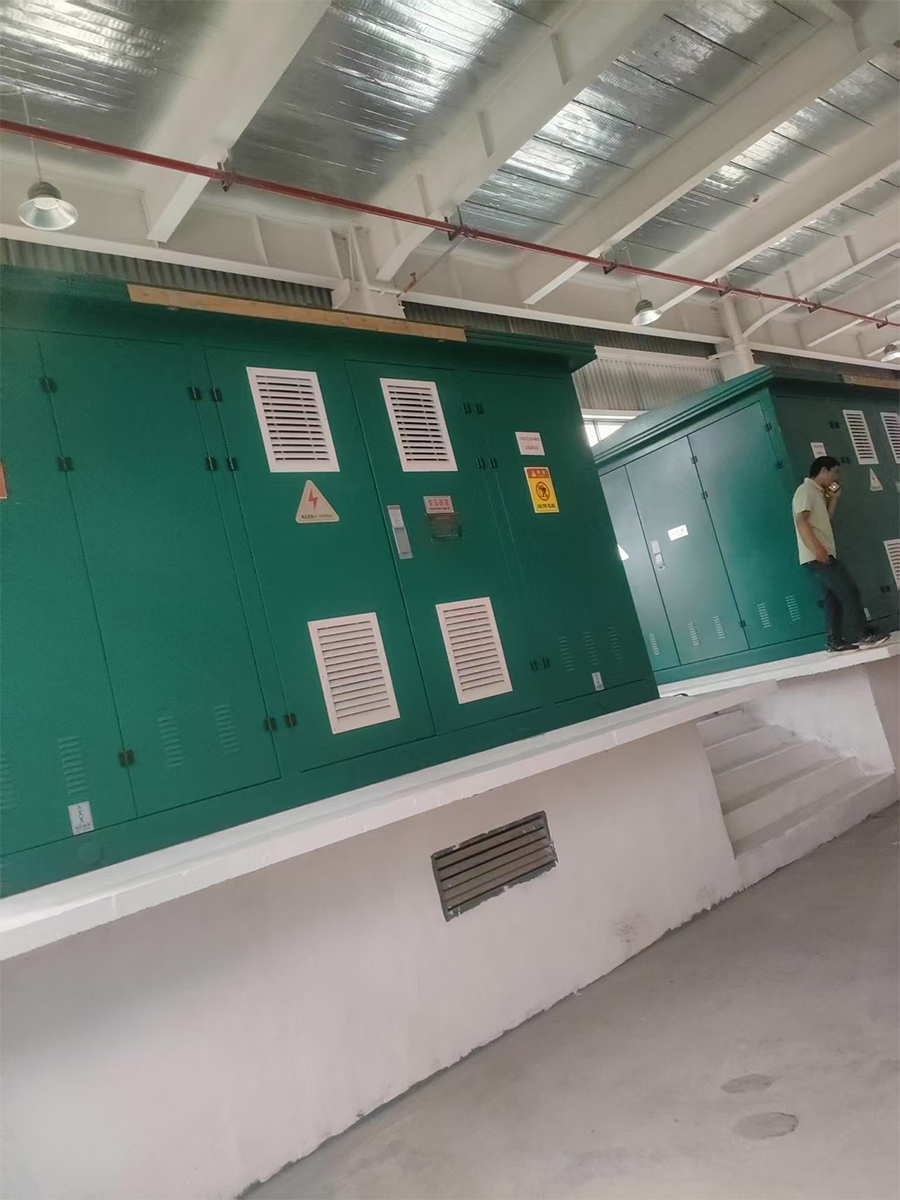 Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
-
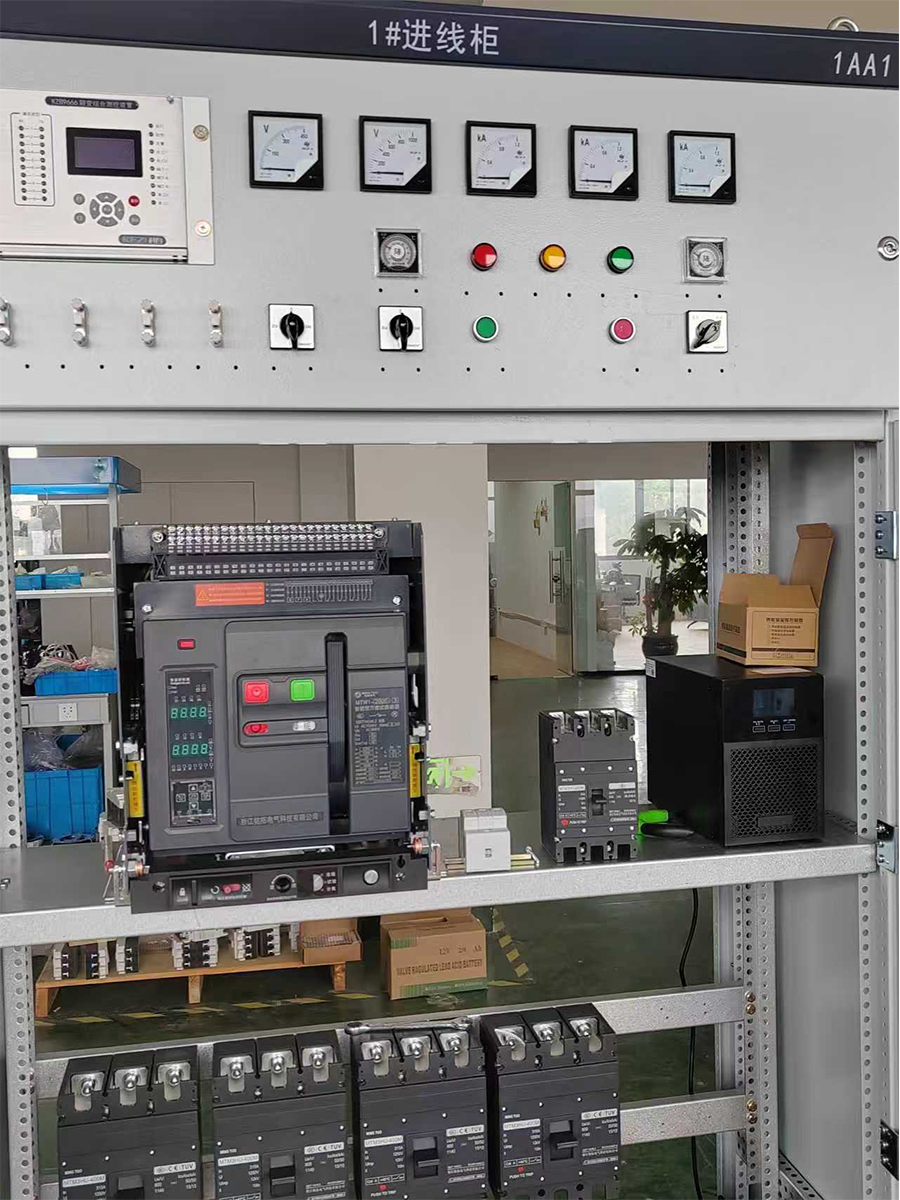 Application Scenario Footage
Application Scenario Footage
-
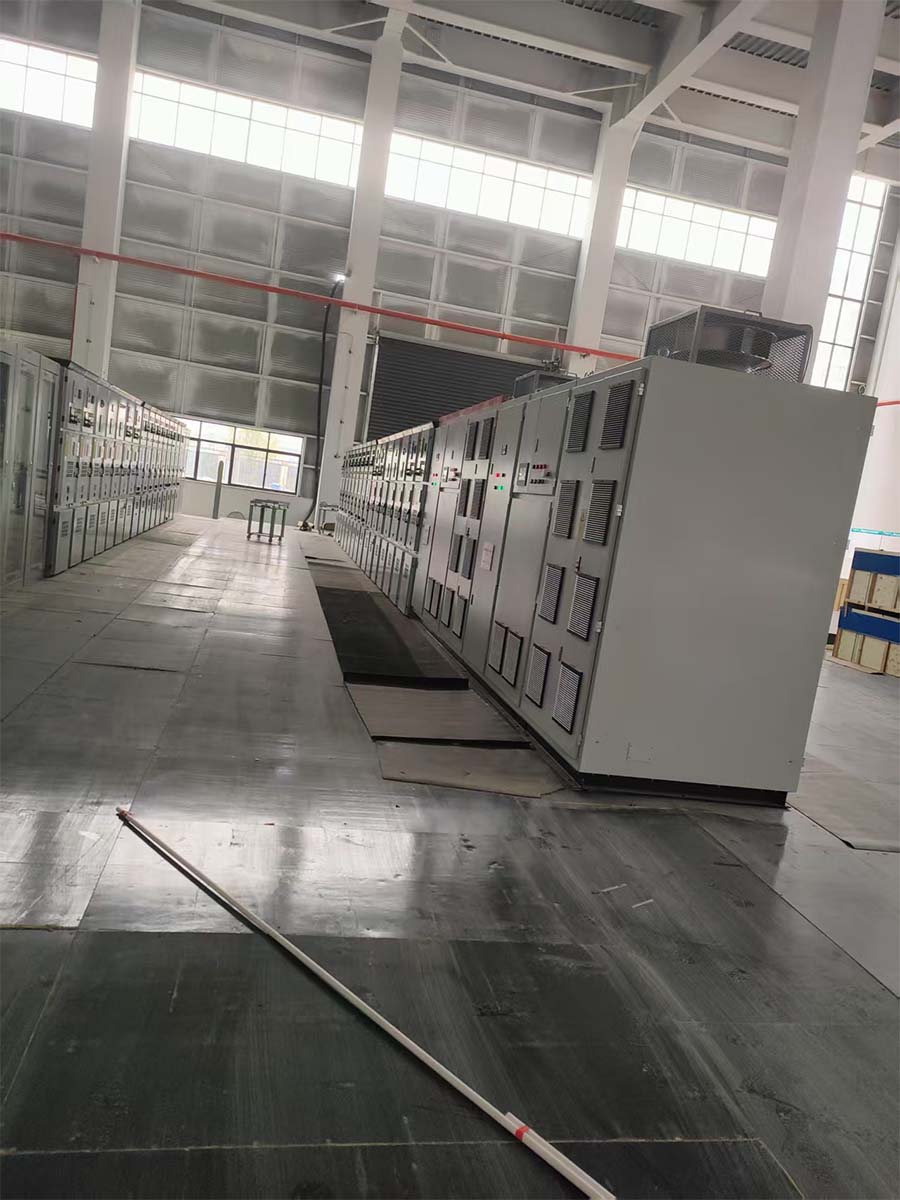 Power transmission successful
Power transmission successful
-
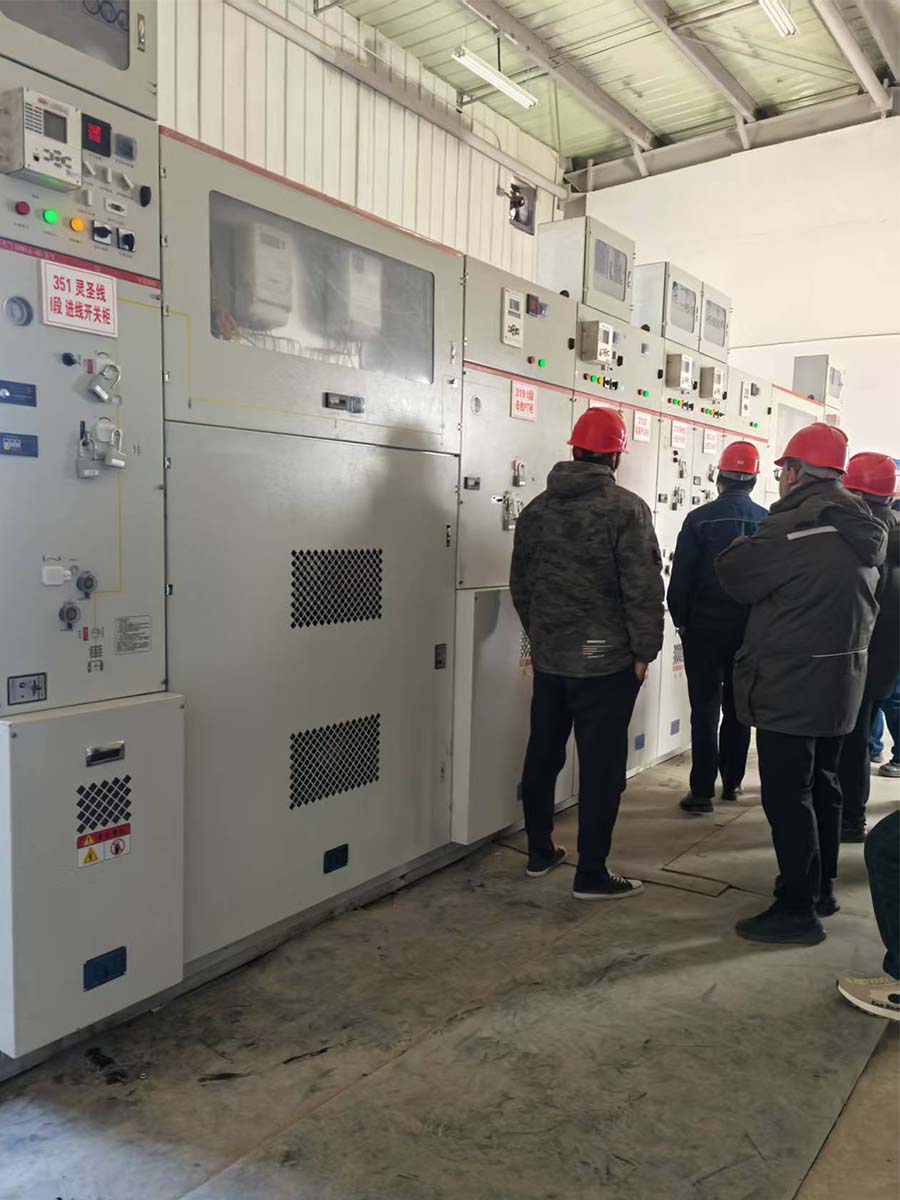 Power transmission successful
Power transmission successful
-
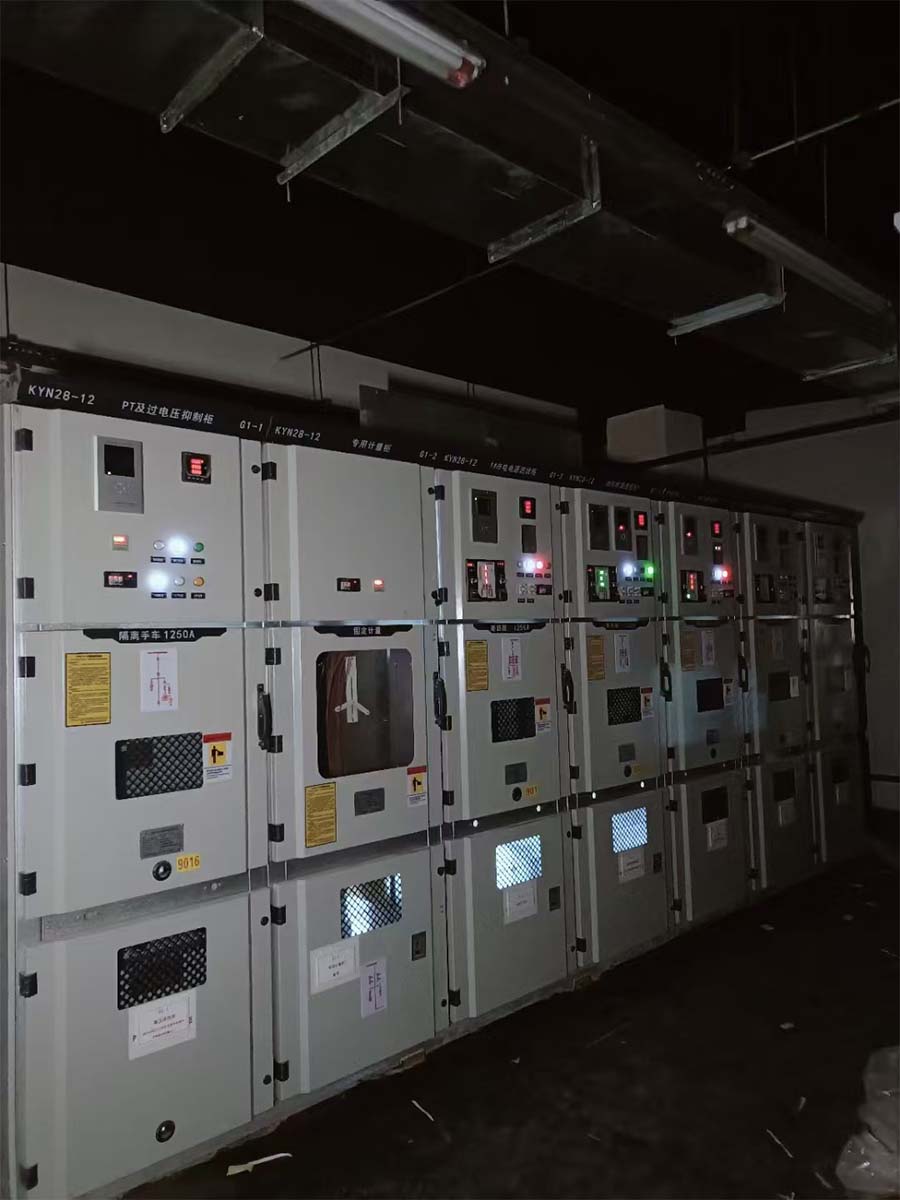 Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Cabinet Utilising ACB and MCCB
Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Cabinet Utilising ACB and MCCB
-
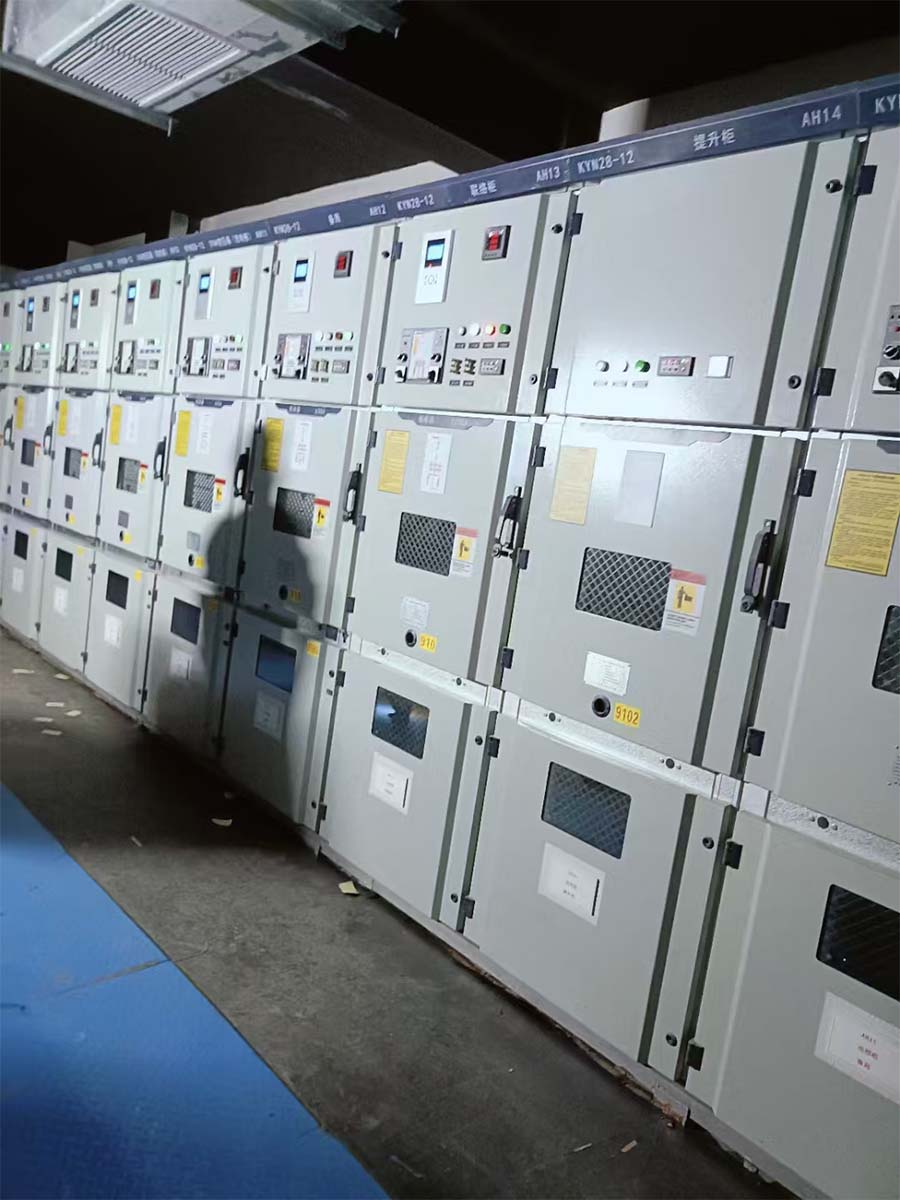 Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Cabinet Utilising ACB and MCCB
Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Cabinet Utilising ACB and MCCB
-
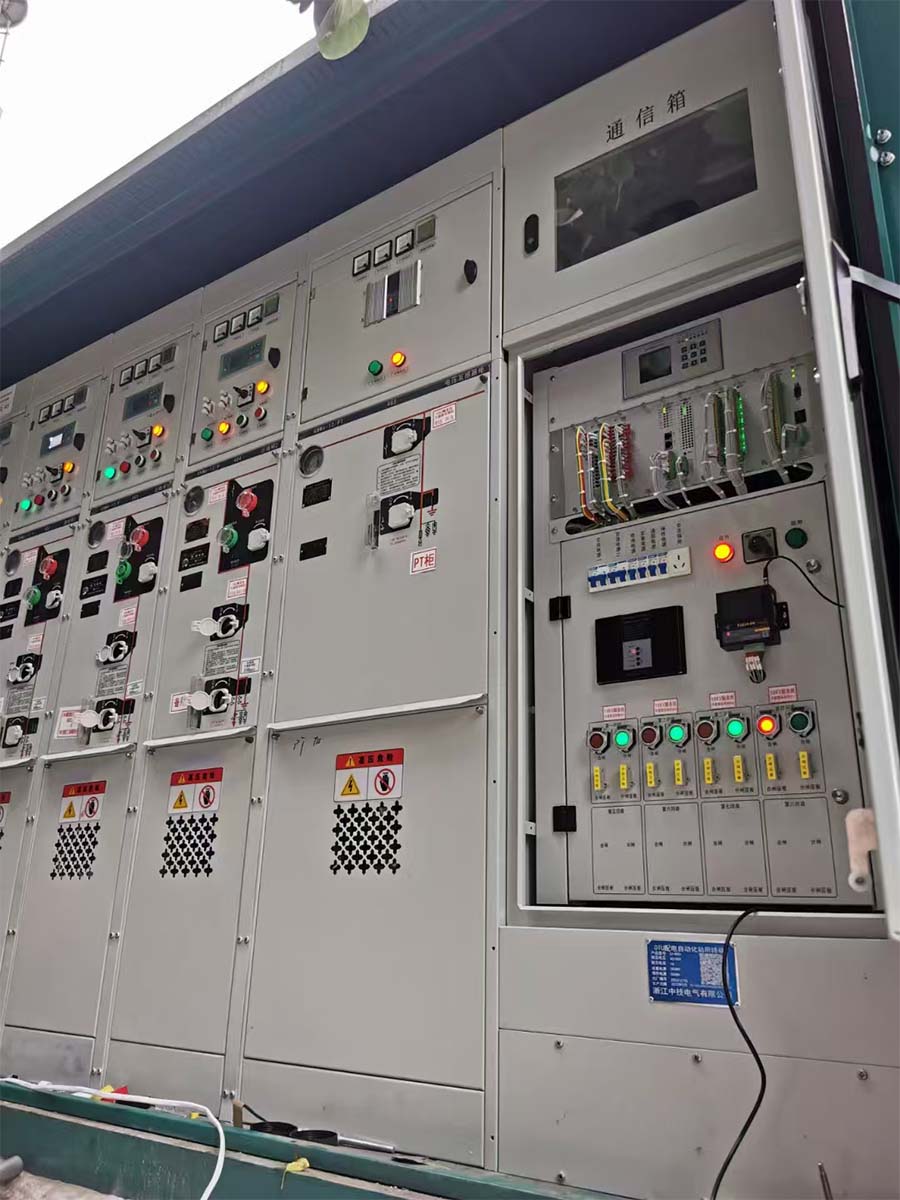 Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
Box-typesubstation ACB VCB MCCB
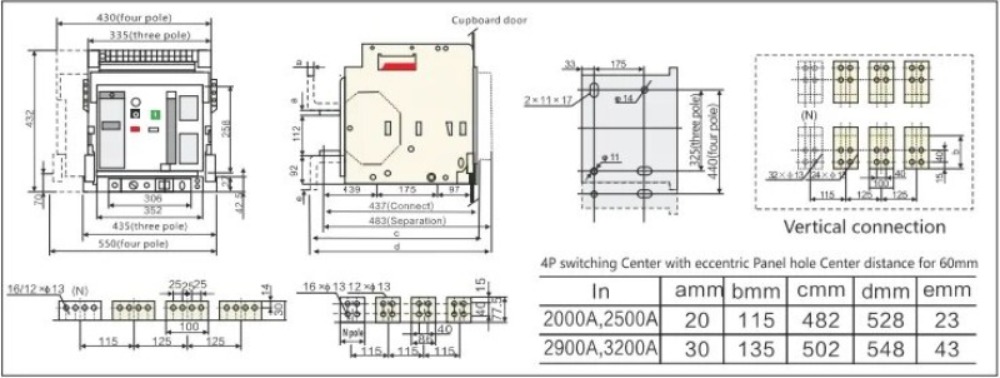
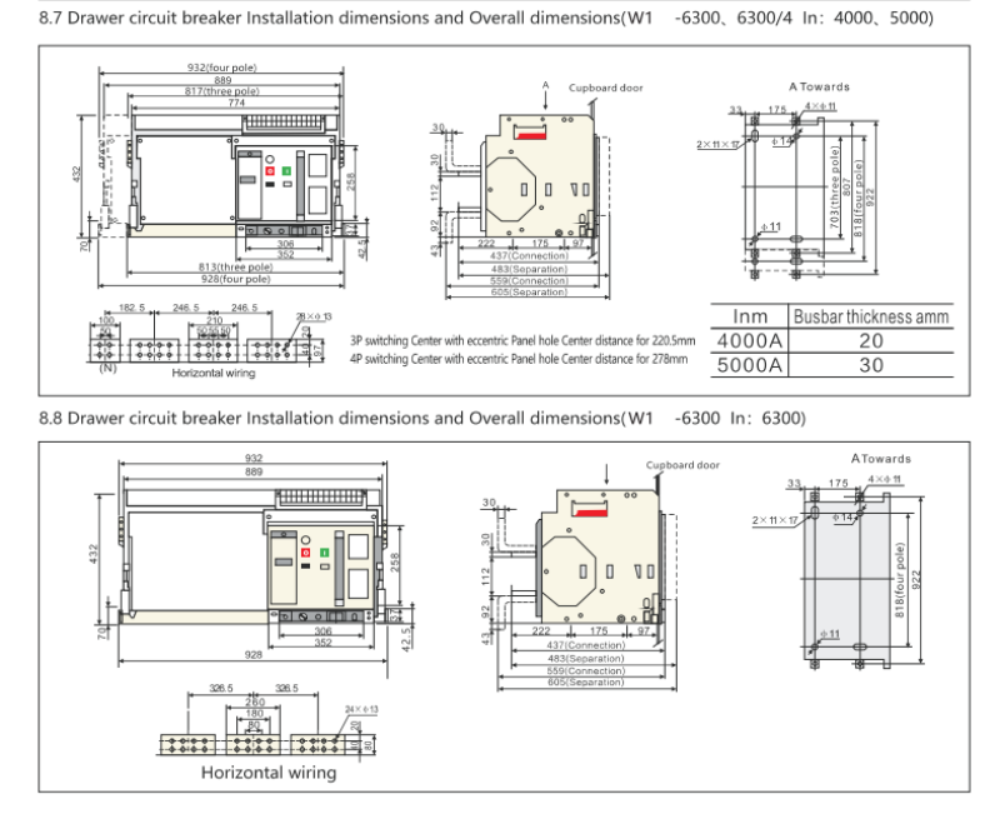
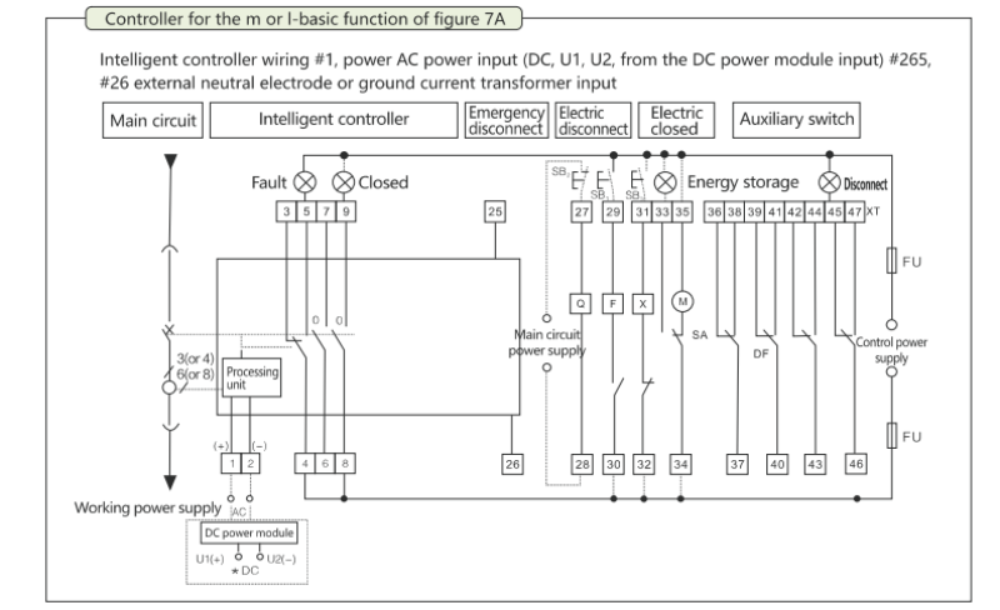
| Model | MTW1-2000 | MTW1-3200 | MTW1-4000 | MTW1-6300 | MTW1-7500 | ||
| Shell current | Inm(A) | 2000 | 3200 | 4000 | 6300 | 7500 | |
| Number of poles | - | 3P / 4P | 3P / 4P | 3P / 4P | 3P / 4P | 3P / 4P | |
| Rated working voltage | Ue(v) | AC400/690 | AC400/690 | AC400/690 | AC400/690 | AC400/690 | |
| Rated current | In(A) | 4.00601E+24 | 2.00025E+15 | 3.20036E+11 | 4.0005E+11 | 7500 | |
| Rated insulation voltage | Ui(v) | 800 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| Rated impulse withstand voltage | Uimp(kv) | 8 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| Controller model | - | L, M, H | L, M, H | L, M, H | L, M, H | L, M, H | |
| Operating frequency | (Hz) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| Rated limit short-circuit breaking capacity | Icu kA (o-co) | 400V | 65 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 120 |
| 690V | 50 | 65 | 75 | 85 | 85 | ||
| Rated running short-circuit breaking capacity | Ics kA (o-co-co) | 400V | 40 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 100 |
| 690V | 40 | 50 | 65 | 75 | 75 | ||
| Rated short time withstand current | IcwkA(1s) Time delay 0.4s o-co |
50 | 65 | 65 | 85 | 85 | |
| Power loss | (In) W | Fixed | 40,60,90,140,170 | 170,260,320,420 | 430,440,450 | 1.22513E+11 | 1.22513E+11 |
| Drawer | 80,130,205,310 | 400,510,650,760 | 780,790,800 | ||||
| Standard | - | GB-TGB14048.2/IEC60947-2 | GB-TGB14048.2/IEC60947-2 | GB-TGB14048.2/IEC60947-2 | GB-TGB14048.2/IEC60947-2 | GB-TGB14048.2/IEC60947-2 | |
| Installation Method | - | Fixed Type (3/4) | Fixed Type (3/4) | Fixed Type (3/4) | Fixed Type (3/4) | Fixed Type (3/4) | |
| Drawer Type (3/4) | Drawer Type (3/4) | Drawer Type (3/4) | Drawer Type (3/4) | Drawer Type (3/4) |

 English
English